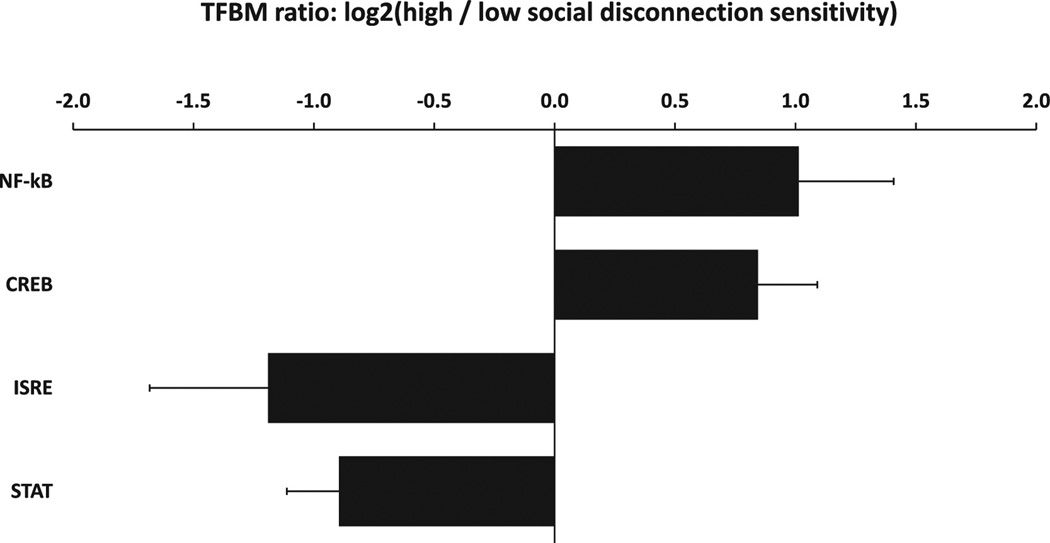
Figure 2.
Bioinformatic analysis of endotoxin-induced activation of pro-inflammatory and antiviral transcription control pathways in PBMC from people with high vs. low levels of sensitivity to social disconnection. Data represent (log2-transformed) ratio of transcription factor-binding motifs (TFBM) for beta-adrenergic-related (CREB), pro-inflammatory (NF-κB), and antiviral (ISRE and STAT) transcription factors in the promoters of all genes showing > 1.2-fold greater magnitude of endotoxin-induced activation over the general range of individual differences in sensitivity to social disconnection (−2SD vs +2SD relative to mean). Differential gene expression was analyzed in continuous (log2) metric, with the 1.2-fold discrete threshold used solely to define a discrete gene set for promoter-based bioinformatics analysis.