Figure 4. Inhibition of ERK5 mimics TS-induced EMT in normal human bronchial epithelial (NHBE) cells.
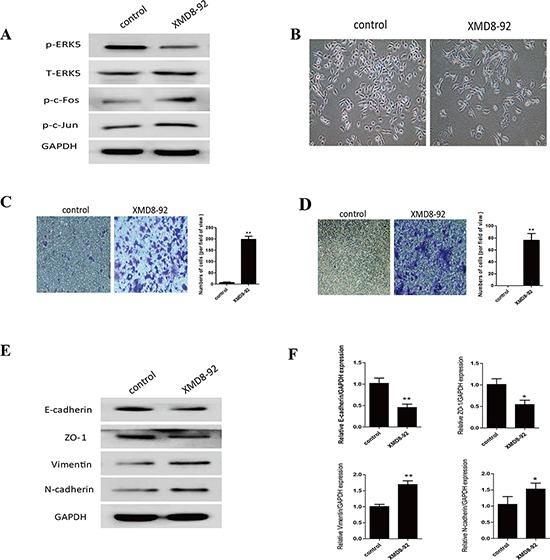
A. ERK5 inhibitor suppressed ERK5 activation in NHBE cells. NHBE cells were treated with a highly specific ERK5 inhibitor (XMD8-92) for 7 days, and Western blot analyses were performed for the measurements of phosphorylated ERK5, phosphorylated c-Fos and phosphorylated c-Jun. B. ERK5 inhibitor triggered morphological change of NHBE cells. C. ERK5 inhibitor enhanced migratory capacity of NHBE cells, as determined by transwell migration assay. D. ERK5 inhibitor increased invasive capacity of NHBE cells, as determined by invasion assay. E. Treatment of ERK5 inhibitor resulted in reduced protein levels of E-cadherin and ZO-1, and increased protein levels of Vimentin and N-cadherin. F. Treatment of ERK5 inhibitor decreased the expression of E-cadherin and ZO-1 mRNAs, and increased Vimentin and N-cadherin mRNAs. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with control group.
