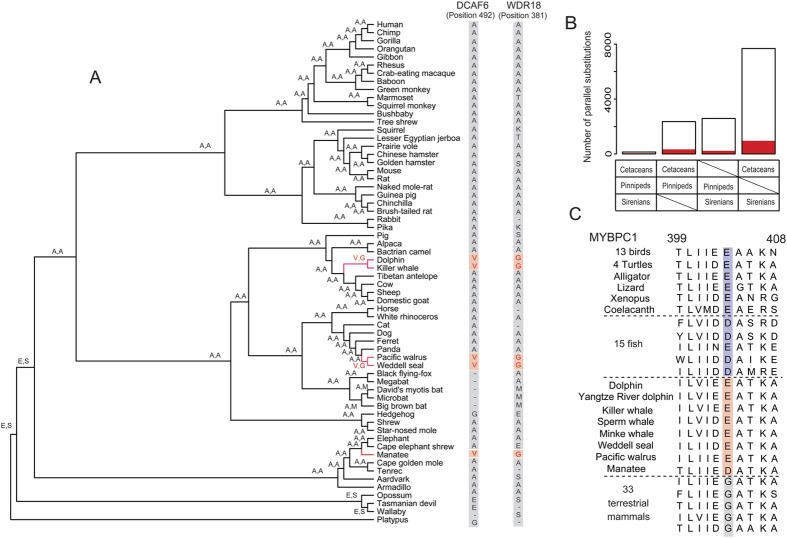
Figure 1. Parallel and unique substitutions in marine mammals.
(A) Parallel substitutions in DCAF6 and WDR18 in marine mammals. We utilized genomic data of 5 marine mammals and 57 terrestrial mammals with completed genomes. Amino acid residues associated with each branch are based on reconstructed ancestor sequences at the corresponding positions in DCAF6 and WDR18. (B) Number of parallel substitutions along the branches of the three marine groups, or at least two marine mammal lineages, since they evolved from a terrestrial ancestor. Parallel substitutions unique to the indicated marine groups are shaded red. (C) Deduced partial amino acid sequence alignment of MYBPC1. The common substitution identified is located at amino acid position 404 of the human ortholog. The corresponding sites in terrestrial mammals are shown in gray, in marine mammals in orange, and in fish, birds, amphibians, and reptiles in blue.