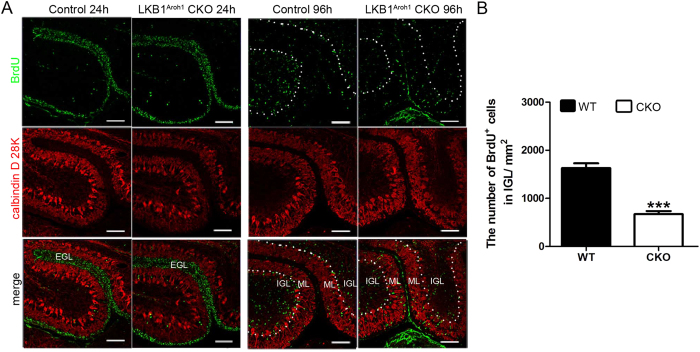
Figure 6. Migration failure of the cerebellar granule cells in the LKB1Atoh1 CKO mice.
(A) BrdU pulse chase experiments at P7. The migration of the GCs in wild-type and LKB1Atoh1 CKO cerebella were analyzed at 24 h and 96 h after the BrdU pulse. BrdU immunostaining was counterstained using CalbindinD28K in sagittal sections of the cerebellum. 24 h after the BrdU pulse, the BrdU+ cells started departing from the EGL and entered the ML, but had not yet reached the IGL, in both the wild-type and mutant cerebellum. 96 h after the BrdU pulse, significant number of the BrdU+ cells were observed in the IGL in the wild-type cerebellum, but much less BrdU+ cells were found in the IGL of the mutant cerebellum. (B) Quantification of BrdU+ cells confirmed that much less BrdU+ cells were found in the IGL of mutant cerebellum compared with the wild-type cerebellum. These observations showed that GC migration was disrupted in the LKB1Atoh1 CKO cerebellum (P = 2 × 10 −4). The error bars indicate the SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 compared to the WT by Student’s t-test; n = 4 animals for each group. Green, BrdU; Red, CalbindinD28K; Blue, DAPI. Scale Bars: 100 μm.