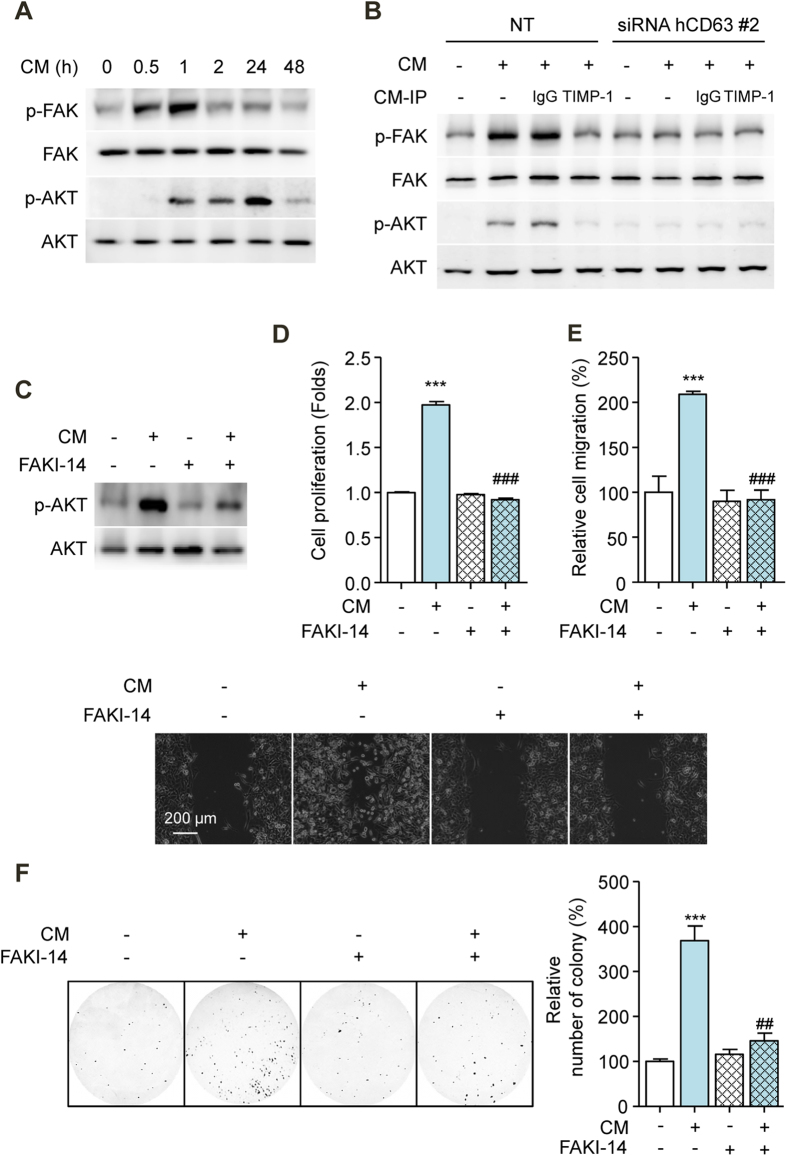
Figure 6. Secreted TIMP-1 Activates the FAK Signal Transduction Pathway in HCC Cells.
(A) Effects of CM on FAK and AKT phosphorylation in SK-HEP1 cells. FAK and AKT were used as references. (B) Effects of CM on FAK and AKT phosphorylation in CD63-siRNA-transfected SK-HEP1 cells. Cells were treated with CM for 1 h (p-FAK and FAK) and 24 h (p-AKT and AKT), respectively. FAK and AKT were used as references. (C) Effects of FAK inhibitor-14 (10 μM, FAKI-14) on AKT phosphorylation in SK-HEP1 cells. Cells were treated with CM in the presence or absence of FAK inhibitor-14 for 24 h. AKT was used as a reference. (D) Effects of FAK inhibitor-14 on the proliferation of SK-HEP1 cells. Cells were treated with CM in the presence or absence of FAK inhibitor-14 for 72 h. (E) Densitometric analysis (up) and representative images (down) of wound-healing assay of SK-HEP1 cells. Cells were treated with CM in the presence or absence of FAK inhibitor-14 for 30 h. Scale bars: 200 μm. (F) Representative images (left) and densitometric analysis (right) of soft agar assay of SK-HEP1 cells. Cells were treated with CM in the presence or absence of FAK inhibitor-14 for 24 h. After treatment, the cells were counted and placed in soft agar for colony assay to determine cell survival. ***p < 0.001 vs. untreated control, ##p < 0.01 vs. CM-treated control, and ###p < 0.001 vs. CM-treated control.