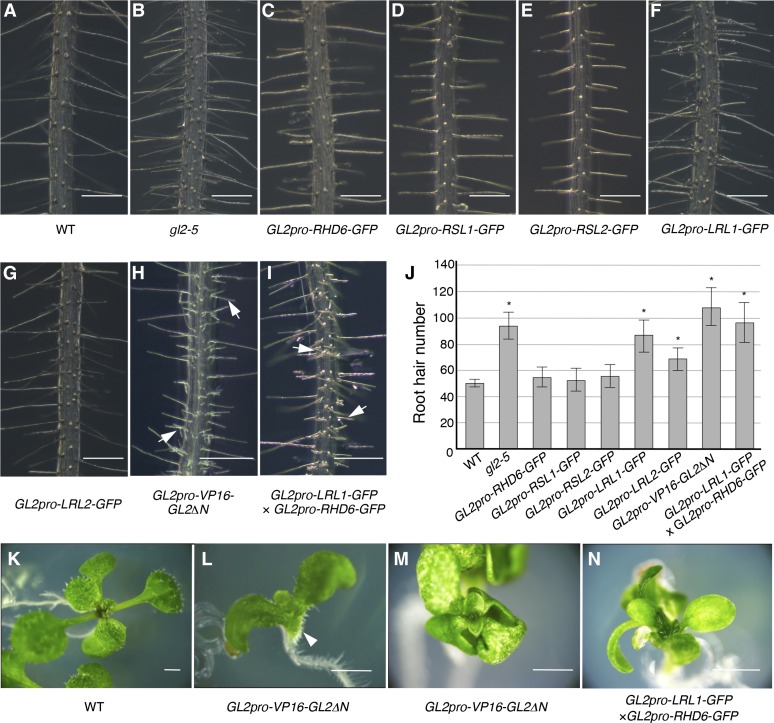
Figure 7.
Phenotypes Caused by the GL2 Promoter-Driven bHLH-GFP Genes.
(A) to (I) Main roots of the wild-type (A) and gl2-5 (B) plants and the transgenic plants harboring GL2pro-RHD6-GFP (C), GL2pro-RSL1-GFP (D), GL2pro-RSL2-GFP (E), GL2pro-LRL1-GFP (F), GL2pro-LRL2-GFP (G), GL2pro-VP16-GL2ΔN (H), and both GL2pro-LRL1-GFP and GL2pro-RHD6-GFP (I) at 7 DAG are shown. Typical branching root hair structures are indicated by arrows in (H) and (I).
(J) Root hair numbers of the wild-type and gl2-5 roots and the transgenic roots harboring GL2pro-RHD6-GFP, GL2pro-RSL1-GFP, GL2pro-RSL2-GFP, GL2pro-LRL1-GFP, GL2pro-LRL2-GFP, GL2pro-VP16-GL2ΔN, and both GL2pro-LRL1-GFP and GL2pro-RHD6-GFP at 7 DAG are shown (mean ± sd, n = 10). Asterisks indicate that the root hair numbers are significantly different from those of the wild type (P < 0.01, Student’s t test).
(K) to (N) Phenotypes of the transgenic seedlings harboring GL2pro-VP16-GL2ΔN and both GL2pro-LRL1-GFP and GL2pro-RHD6-GFP in aerial organs. Seedlings of the wild type (K) and transgenic lines harboring GL2pro-VP16-GL2ΔN ([L] and [M]) and both GL2pro-LRL1-GFP and GL2pro-RHD6-GFP (N) are shown. The root hair-like structures on the abaxial surface of the hypocotyl/cotyledon junction are indicated by an arrowhead in (L).
Bars = 250 μm in (A) to (I) and 1 cm in (K) to (N).