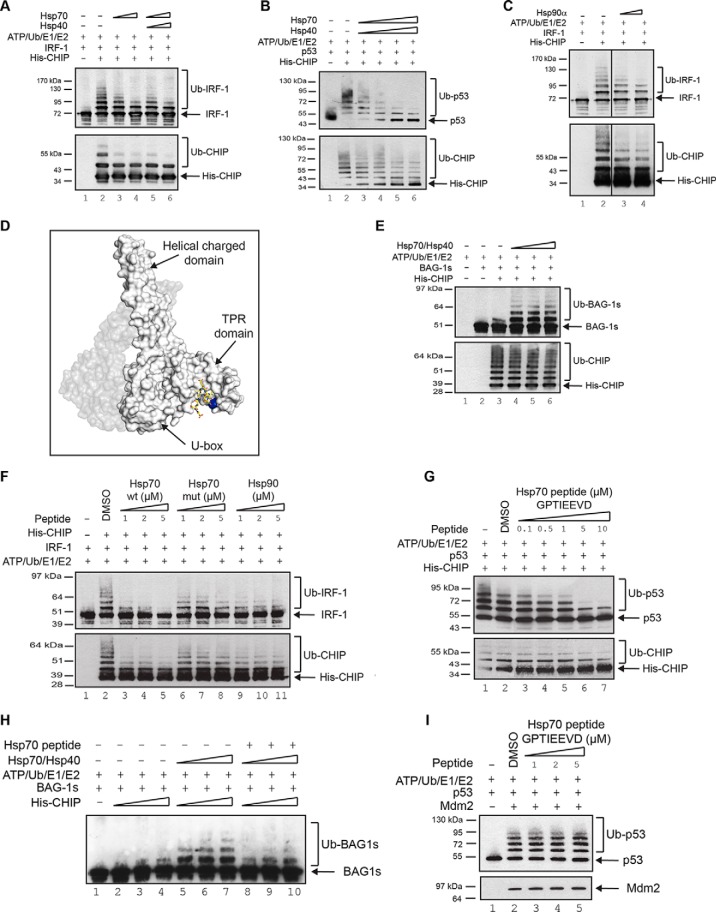
Fig. 1.
Hsp70 differentially modulates CHIP-dependent ubiquitination. (A, C) Immunoblot of in vitro ubiquitination reactions assembled using ATP, ubiquitin, UBE1, UbcH5a, His-CHIP and GST-IRF-1 in the presence of a titration of Hsp70 with or without Hsp40 (A) or Hsp90 (C) at either a 1:1 or 1:2 molar ratio of Hsp70/Hsp90 with CHIP. (B, E) Immunoblot of in vitro ubiquitination assays assembled as in (A) except using untagged p53 (B) or GST-BAG-1s (E) as substrate, in the presence of Hsp70 and Hsp40. (D) Snapshot of the crystal structure of mCHIP dimer (protomers in shades of gray) in complex with Hsp90 peptide (yellow sticks; PDB code 2C2L) generated using PyMOL v1.4.1. Lys30 is highlighted in blue. (F, G) Immunoblot of in vitro ubiquitination reactions assembled using ATP, ubiquitin, UBE1, UbcH5a, His-CHIP and His-IRF-1 (F) or untagged p53 (G) in the presence of a titration of Hsp70 (wt: GPTIEEVD; mut: GAAAEEVD) or Hsp90 (DTSRMEEVD) peptide as indicated. A carrier only control (DMSO) was included. (H) As above, except that GST-BAG-1s was used as the substrate and both full-length Hsp70/Hsp40 as well as Hsp70 wt peptide were included in the assay as indicated. (I) As in (G) except using GST-Mdm2 as the E3 ligase.