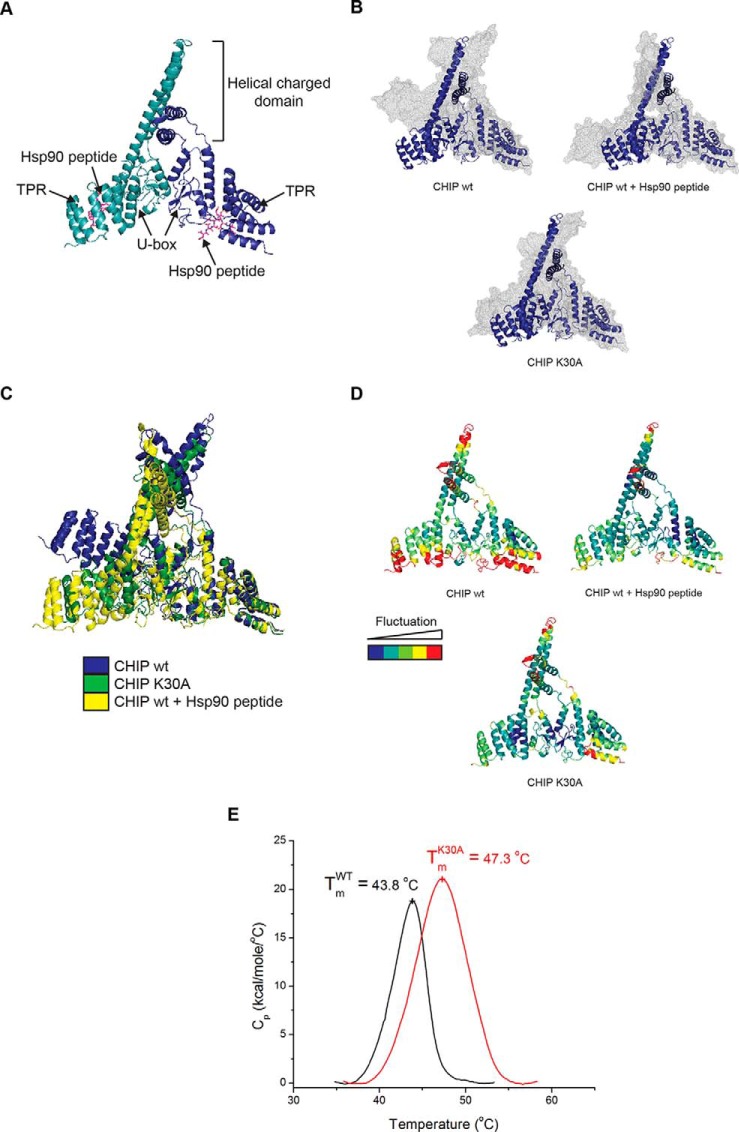
Fig. 4.
CHIP-K30A and Hsp70-bound CHIP have similar equilibrium structures. (A-D) Images were generated using PyMOL v.1.4.1. (A) Crystal structure of murine CHIP dimer (monomers in shades of blue) in complex with Hsp90 peptide (pink sticks; adapted from PDB 2C2L). (B) Overlay of the CHIP dimer before (blue ribbon) and after (gray mesh) 20 ns MD simulations for unliganded CHIP wt (upper left), CHIP wt in complex with Hsp90 peptide (upper right) and CHIP-K30A (bottom). (C) Overlaid snapshots of the CHIP dimer in apo and liganded forms and with Lys30 mutated to Ala after 20 ns MD simulations (from (B)). (D) Root mean square fluctuation (RMSF) of Cα obtained from the trajectories of the 20 ns simulations of CHIP wt ± peptide and the CHIP-K30A mutant. The score of the positional fluctuation analysis averaged over amino acid were color coded and indicated on the crystal structure. (E) For differential scanning calorimetry, protein and buffer controls were heated at a rate of 60 °C/hour from 5 to 85 °C. The thermal transition mid-point (Tm) and specific heat capacities (Cp) were determined using the instrument software (Origin, version 7.0).