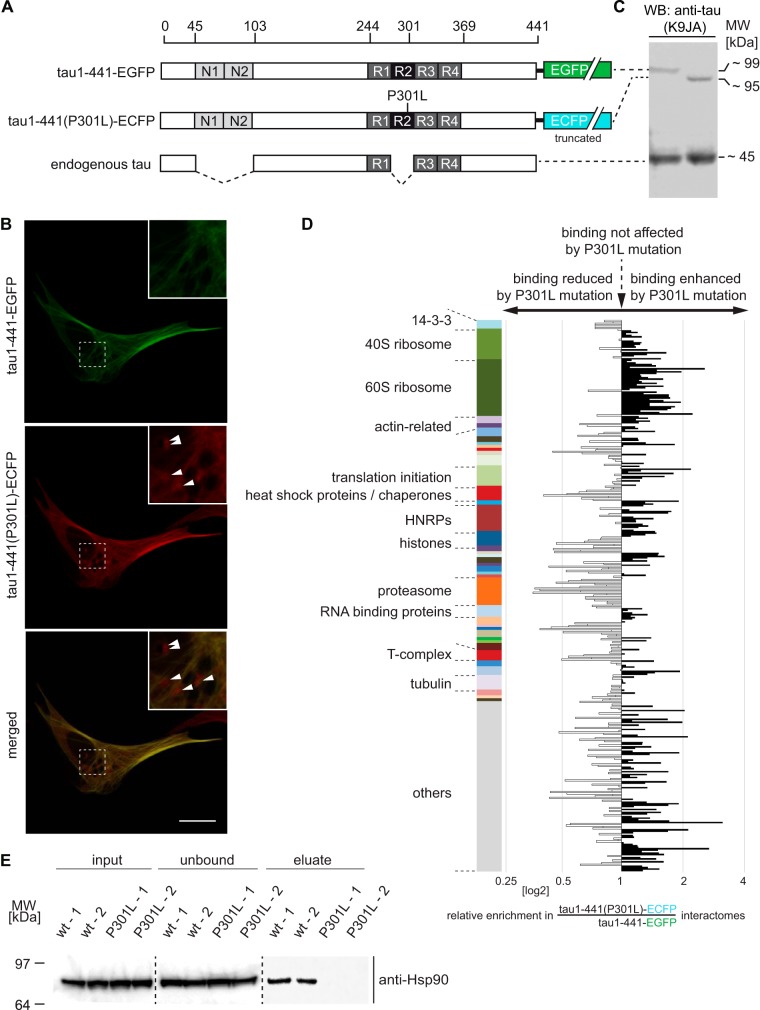
Fig. 4.
Comparative interactome analysis of wild-type and P301L mutant tau. A, Schematic depicting full-length tau expression constructs used in this experiment as well as the principal tau isoform observed in undifferentiated SH-SY5Y cells (73). B, Representative live-cell images of CV-1 cells co-expressing tau1–441-EGFP and tau1–441(P301L)-ECFP. Note the presence of cytosolic punctae (indicated by white arrowheads) only in the ECFP fluorescence channel (pseudo colored in red for improved visibility); scale bar = 1 μm. C, Western blot analysis of total tau levels following transient transfection with K9J8 anti-tau antibody. As previously reported, P301L mutant tau migrated with lower apparent molecular mass than the corresponding wild-type tau construct (74). Note that the heterologous tau levels were comparable to endogenous tau levels in cells that were successfully transfected, because the transfection efficiency we typically achieve with SH-SY5Y cells is around 30% (as determined by the percentage of EGFP-positive cells). D, Graph depicting the relative co-enrichment of proteins together with wild-type or P301L mutant tau. Note the reduced binding of heat shock proteins and proteasomal subunits toward tau1–441(P301L) mutant tau (relative to tau1–441-EGFP). Color bar as in Fig. 3, Panels B and C. E, Validation of selective enrichment of Hsp90 with tau1–441 but not with tau1–441(P301L). Equal volumes of cellular extracts set aside before (input) or after (unbound) GBP-based tau affinity capture, or following elution (eluate) were analyzed by Western blotting and probed with anti-Hsp90 antibody.