Fig. 3.
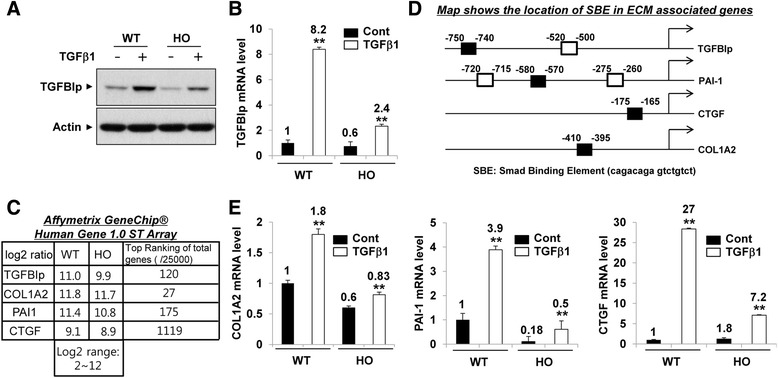
TGFβ1-induced expression of TGFBIp and ECM-associated genes in wild-type and GCD2-homozygous corneal fibroblasts. a, b Serum-depleted wild-type and GCD2 corneal fibroblasts were stimulated with TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml) for 8 h, and protein and mRNA levels of TGFBIp were analyzed by western blot (a) and RT-qPCR (b). b Gene expression was normalized to that of GAPDH (internal control). Results are expressed as fold stimulation relative to the wild-type control (mean ± standard error (SE); **P < 0.01 vs. wild type, n = 3). c Total mRNA was isolated from wild-type and GCD2-homozygous corneal fibroblasts, and gene-expression profiles were assessed using an Affymetrix gene chip. Expression of TGFBIp and ECM-associated genes (COL1A2, CTGF, and PAI-1) is presented as the log2 ratio. d Map shows the locations of Smad binding elements (SBEs) and the primers used for ChIP-qPCR of the TGFBIp, COL1A21, CTGF, and PAI-1 gene promoters. Open and filled boxes are Smad binding elements. Filled boxes are real engaged positions of Smad in corneal fibroblast. e Serum-depleted wild-type and GCD2-homozygous corneal fibroblasts were stimulated with TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml) for 8 h, and mRNA levels of ECM-associated genes (COL1A2, CTGF, and PAI-1) were analyzed by RT-qPCR. Gene expression was normalized to that of GAPDH (internal control), and results are expressed as fold stimulation over the wild-type control (mean ± standard error (SE); **P < 0.01 vs. wild type, n = 3)
