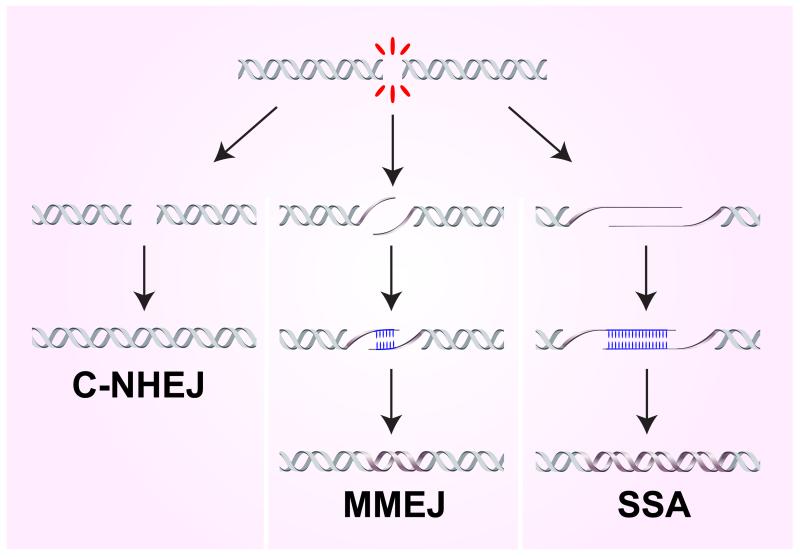
Figure 1. Mechanisms of end joining.
Classical non-homologous end-joining (C-NHEJ) involves no homology or only 1-4 nucleotides of homology at the junction; microhomology mediated end-joining (MMEJ) requires 1-16 nt of homology internal to the ends to align them for repair; and single-stranded annealing (SSA) involves annealing between more extensive homologies provided by direct repeats flanking the DSB. MMEJ and SSA are both highly mutagenic due to loss of one repeat and the intervening sequence.