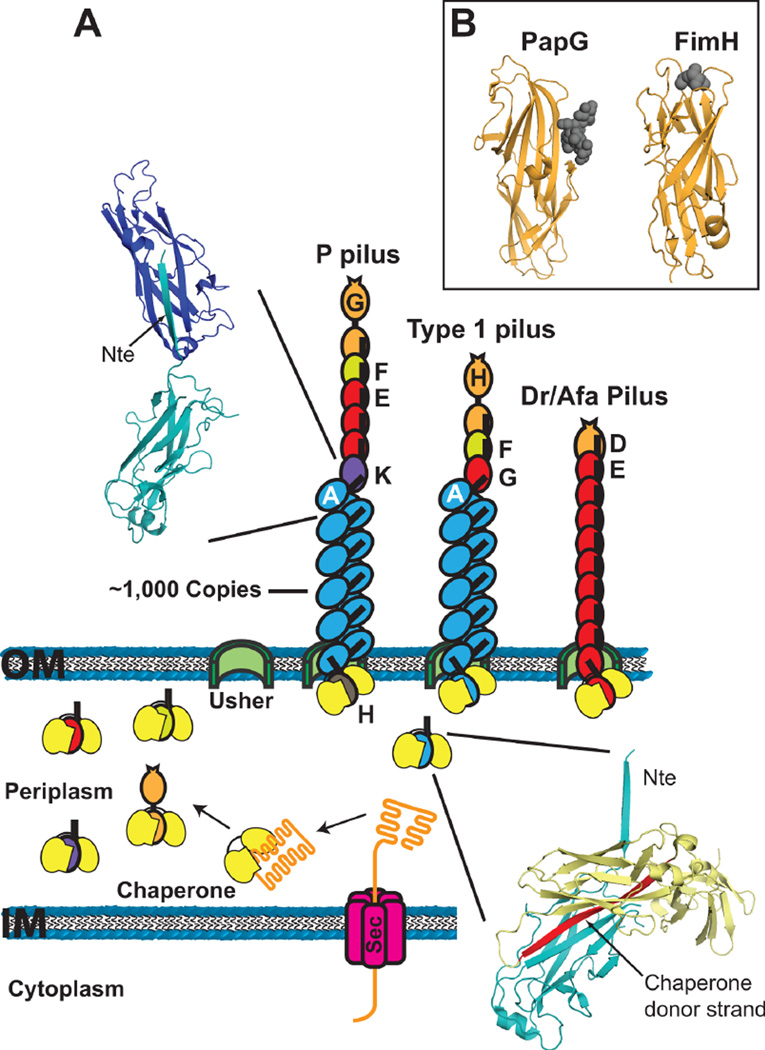
Figure 2.
(A) Model for pilus biogenesis by the CU pathway. Pilus subunits enter the periplasm as unfolded polypeptides via the Sec system. Subunits fold upon forming binary complexes with the periplasmic chaperone (yellow). The crystal structure in the lower right depicts the chaperone-subunit donor strand exchange reaction (PapD-PapA; PDB ID: 2UY6), with the chaperone donor strand indicated in red. Pilus assembly takes place at the outer membrane usher, which catalyzes the exchange of chaperone-subunit for subunit-subunit interactions. Models for assembled P, type 1 and Afa/Dr pilus fibers are shown. The crystal structure in the upper left depicts the subunit-subunit donor strand exchange reaction that occurs in the pilus fiber (PapA-PapA; PDB ID: 2UY6), with the Nte donor strand indicated. (B) Crystal structures of the PapG (P pili; PDB ID: 1J8R) and FimH (type 1 pili; PDB ID: 1KLF) adhesin domains with bound globoside and mannose, respectively. The sugars are depicted as dark gray spheres.