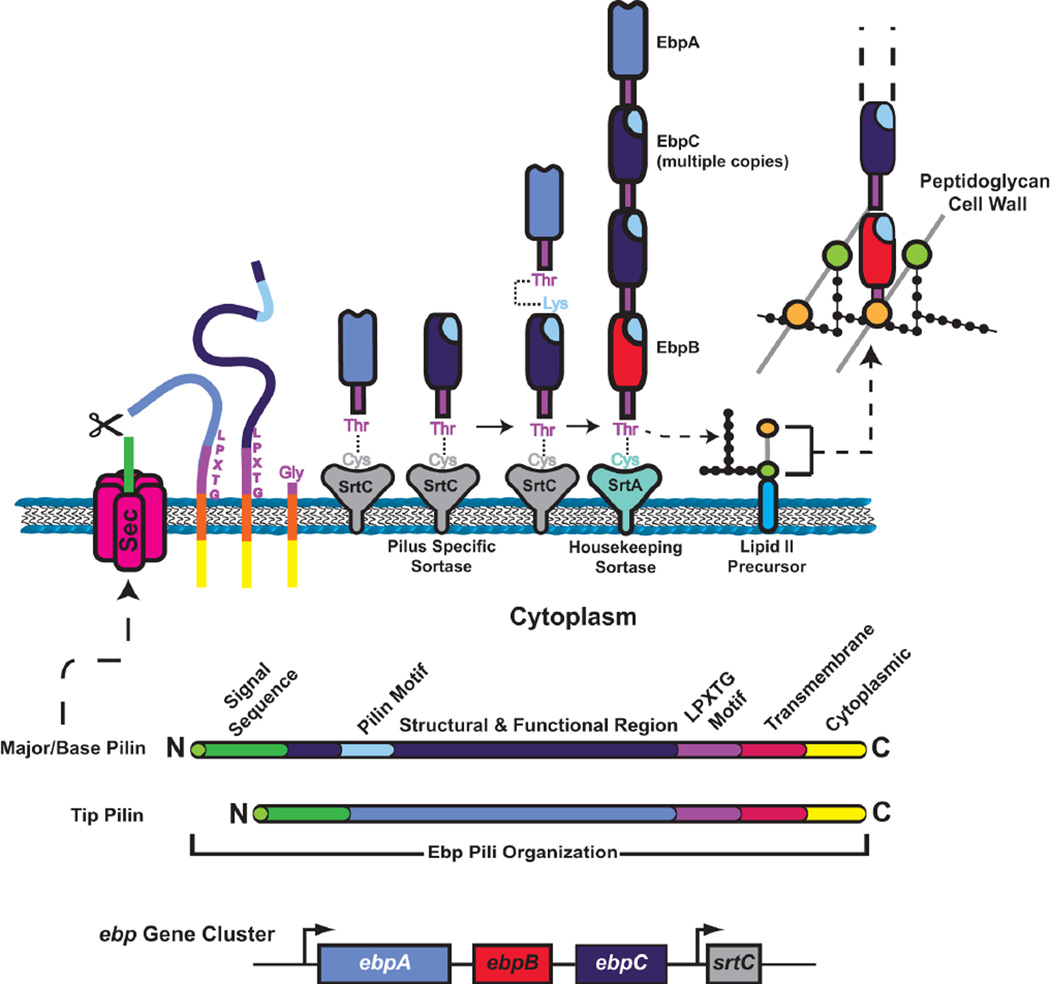
Figure 9.
Model for Gram-positive pilus polymerization and incorporation into the cell wall. The domain organization of typical major and minor pilins is shown at the bottom, along with the ebp gene cluster coding for Ebp pili of E. faecalis. The steps of secretion across the cytoplasmic membrane and covalent linkage to a sortase are the same as for MSCRAMMs, except the pilins are processed by the SrtC pilus-specific sortase. Pilus subunits are polymerized by formation of intermolecular isopeptide bonds between the Lys of a pilin motif of one subunit and the Thr of the LPXTG motif of a preceding subunit in the fiber. Linkage to the cell wall occurs when a growing pilus fiber is transferred to a base pilin bound to the SrtA housekeeping sortase. Integration of the pilus into the cell wall follows the mechanism as described for MSCRAMMs.