Figure 5.
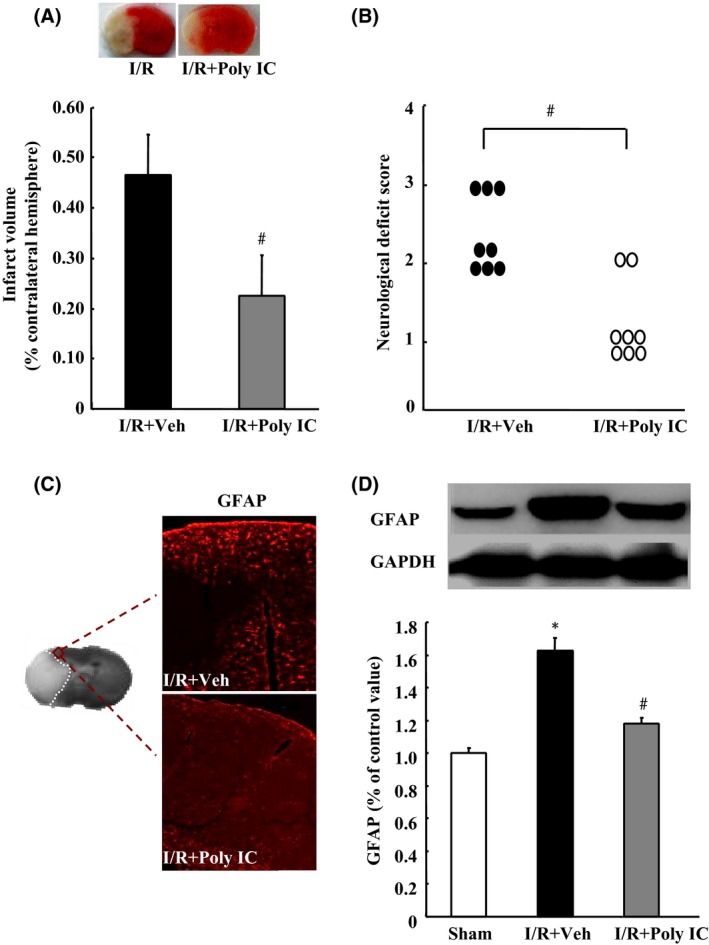
Poly IC attenuates cerebral ischemia–reperfusion (I/R)‐induced brain damage and astrocyte proliferation in rats. Poly IC (1.25 mg/kg) or normal saline was administrated by intraperitoneal injection at the onset of reperfusion and at 1, 3, and 5 days after cerebral I/R (I/R+Poly IC and I/R+vehicle [Veh], respectively). (A) Representative 2,3,5‐triphenyltetrazolium chloride‐stained brain sections (2 mm thick) and quantification of the total infarct volume at 7 days postreperfusion. (B) Neurological function of rats after I/R injury, as evaluated by the Zea‐Longa method. (C) Representative images of GFAP immunostaining in the ischemic penumbra. (D) Immunoblot analysis of GFAP expression. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM; n = 6–8 per group. *P < 0.05 versus sham group; # P < 0.05 versus I/R+Veh group.
