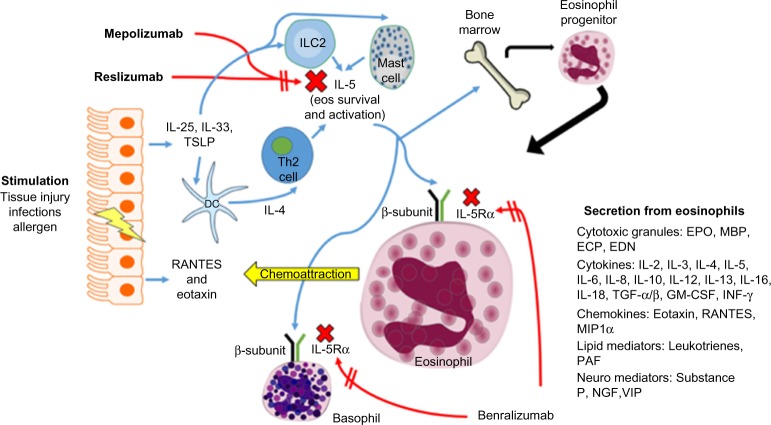
Figure 1.
Eosinophil (eos) trafficking and maturation in asthma.
Notes: Stimulation at the epithelial cell surface leads to the generation of cytokines and chemokines that increase production of IL-5. Generation of IL-5 by Th2 cells, ILC2, and mast cells is essential in eosinophil survival and activation in peripheral tissue. This figure also shows the mechanisms of action for mepolizumab, reslizumab, and benralizumab, as well as the secretory products of eosinophils. Red arrows represent inhibitory pathways, while blue arrows are activating pathways.
Abbreviations: EDN, eosinophil-derived neurotoxin; ECP, eosinophil cationic protein; EPO, eosinophil peroxidase; IL, Interleukin; TGF-α/β, transforming growth factor-α/β; INF-γ, interferon gamma; RANTES, regulated upon activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted; MIP1α, macrophage inflammatory proteins-1α; PAF, platelet-activating factor; VIP, vasoactive intestinal peptide; NGF, nerve growth factor; TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin; ILC2, innate lymphoid cells (type 2).