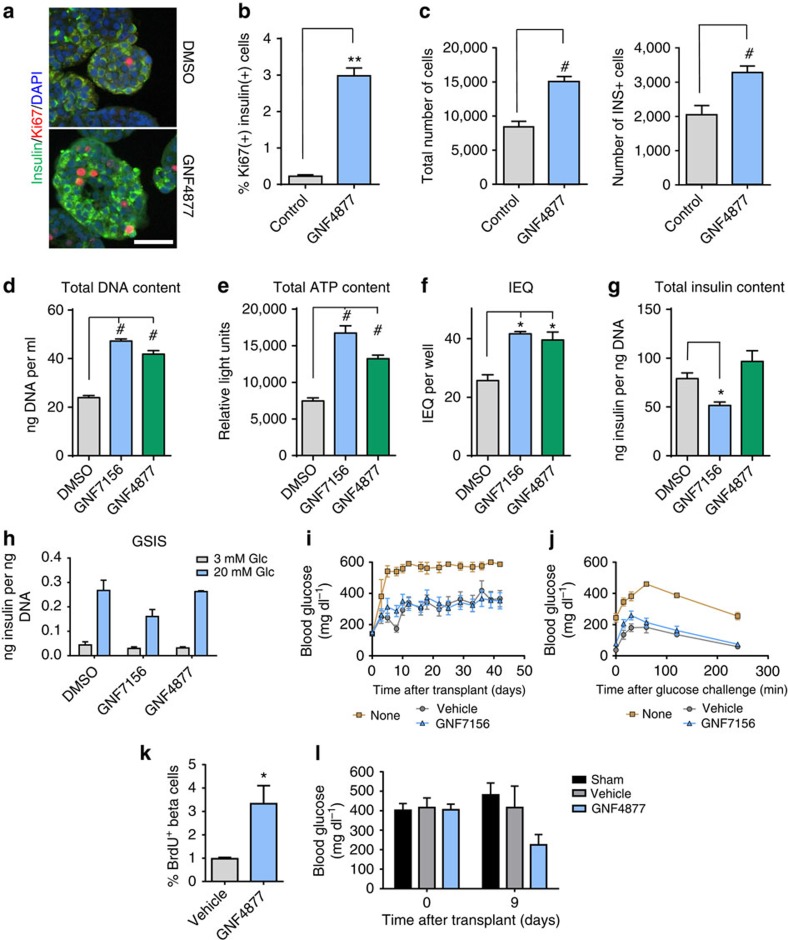
Figure 2. AP compounds expand human islets ex vivo with retention of function after transplantation.
(a–c) Treatment of intact primary human islets with GNF4877 for 8 days results in increased beta cell numbers relative to vehicle control–treated islets. (a) Immunofluorescence for insulin, Ki67 and DAPI on DMSO or GNF4877-treated human intact islets (scale bar, 50 μm). (b) Quantification of Ki67+ as a percent of total insulin+ cells (n=3). (c) Total number of islet cells and total number of insulin+ cells after 8 days of treatment of human islets with GNF4877 or vehicle (n=24 islets; bars represent mean±s.d.; **P<0.01, #P<0.0001, Student's t-test. (d–j) Primary human islets were treated for 7 days with the AP compounds or vehicle control (6.7 μM GNF7156 or 2 μM GNF4877; n=9 per condition) and then tested for (d) total DNA content, (e) total ATP content, (f) islet equivalent units (IEQ), (g) total insulin content and (h) glucose stimulated insulin release (GSIS) (*P<0.05, #P<0.0001, Student's t-test). (i–j) GNF7156 and DMSO-expanded human islets are functionally equivalent when equal numbers were transplanted into the kidney capsule of STZ-induced diabetic NOD–SCID mice: (i) Fed blood glucose and (j) oral glucose tolerance test. Data are shown as mean±s.d. (six mice per group; transplanted with islets from a single human donor). (k–l) NSG mice were transplanted with a sub-optimal dose of human islets under the kidney capsule before treatment with GNF4877 (oral, 50 mg kg−1, twice daily) or vehicle control. GNF4877-treated NSG mice transplanted with human islets demonstrated increased BrdU incorporation into insulin-positive cells by immunohistochemistry (k) and display improved glucose control as measured by fed glucose levels (l). Data shown as mean±s.d.; (n=6 mice/group, *P<0.05, Student's t-test).