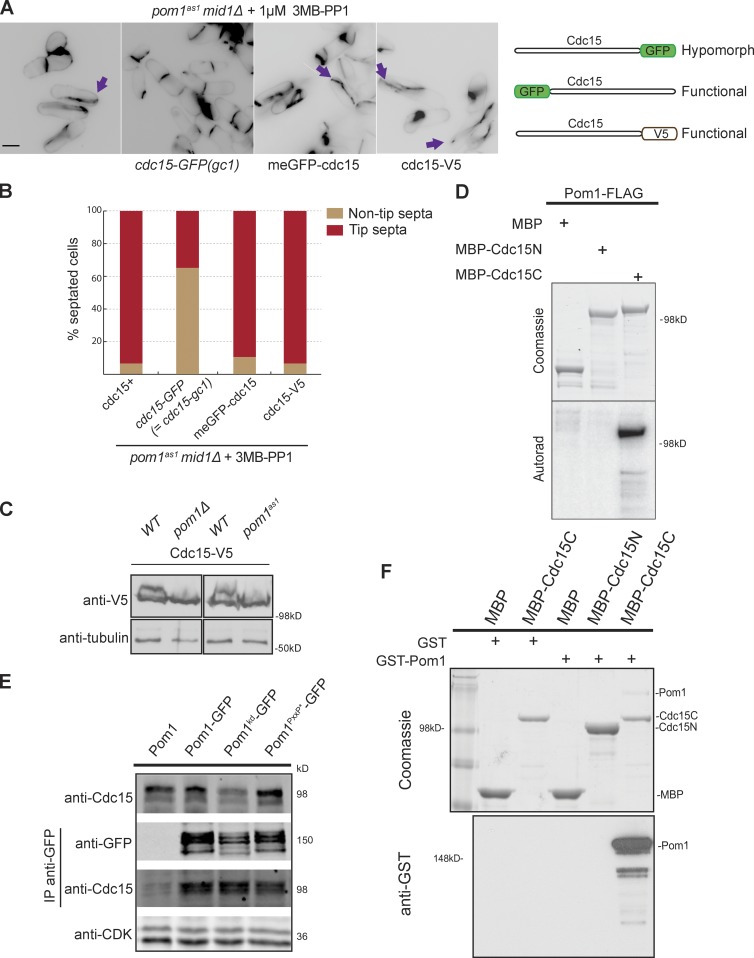
Figure 2.
Pom1 phosphorylates and binds the F-BAR protein Cdc15. (A) Compromising Cdc15 function rescues tip septation in pom1as1 mid1Δ cells. Cells of indicated genotypes were treated with 1 µM 3MB-PP1 for 2 h at 25°C and stained with calcofluor. Arrows indicate tip septa. Bar, 5 µm. The three tagged cdc15 alleles used are schematically shown on the right. (B) Quantification of tip septa in septated cells treated as in A (n > 250). (C) Cdc15 is phosphorylated in a Pom1-dependent manner in vivo. Cdc15-V5 was detected after Western blotting using anti–V5-HRP antibodies in indicated backgrounds. 1 µM 3MB-PP1 was added to the two samples on the right. Tubulin is used as loading control. (D) In vitro kinase assays performed with immunoprecipitated Pom1-FLAG and recombinant MBP-Cdc15N and MBP-Cdc15C. Phosphorimager detection of 32P incorporation (bottom) and Coomassie-stained gels of substrates input, including the MBP-only control (top) are shown. (E) Coimmunoprecipitation of Cdc15 with Pom1-GFP, Pom1kd-GFP, and Pom1PxxP*-GFP precipitated using anti-GFP antibodies. The top blot shows the input, the two middle blots show the anti-GFP IP. CDK was used as a loading control in the bottom blot. (F) In vitro binding assays between Pom1 and Cdc15 using purified recombinant MBP, MBP-Cdc15C, and MBP-Cdc15N incubated with recombinant GST or GST-Pom1. Amylose beads were washed and bound proteins were run on SDS-PAGE and detected by Coomassie staining (top) and anti-GST antibodies (bottom).