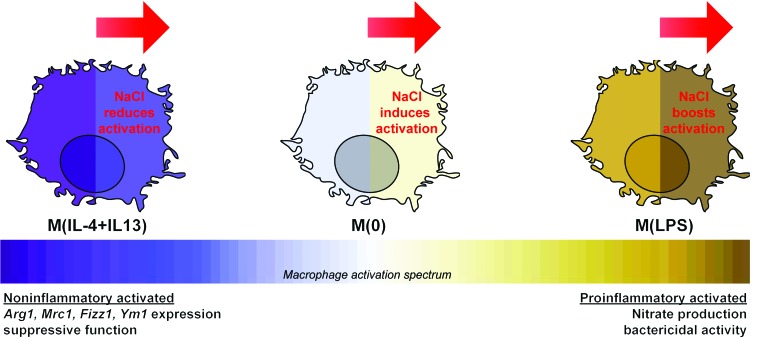
Figure 10. Summary of the effect of high NaCl on the activation of macrophages.
In the presence of noninflammatory signals (e.g., IL-4 and IL-13), this study has shown that NaCl reduces macrophage activation. In contrast, with a proinflammatory stimuli (e.g., LPS), salt augments macrophage activation (18). Furthermore, without a stimulus, M(0) macrophages exhibit an altered homeostasis. Together, we hypothesize that NaCl does not have a general and nonspecific effect on macrophages homeostasis, but rather, its effect is orchestrated via modulating specific signaling pathways and cellular processes essential for macrophage activation.