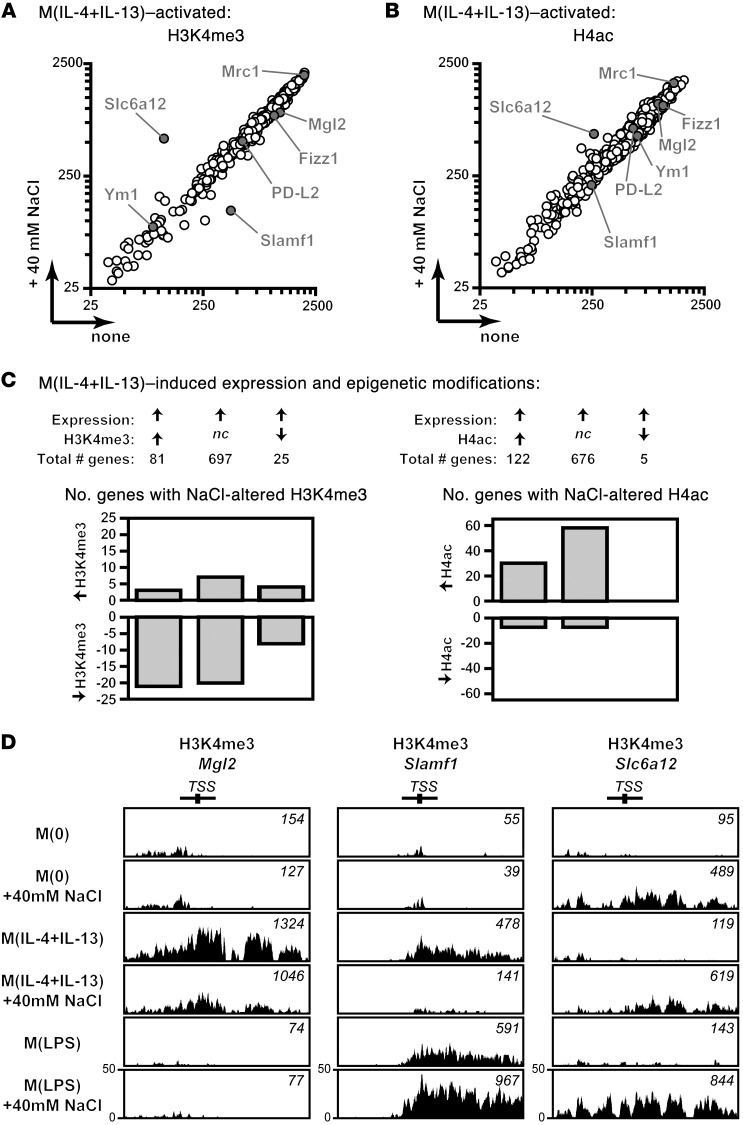
Figure 7. Salt modifies epigenetic marks of M(IL-4+IL-13) genes.
(A and B) ChIP-seq was performed to identify the effect of salt on transcriptionally activating epigenetic modifications upon M(IL-4+IL-13) induction. Only genes that had a corresponding increased gene expression upon M(IL-4+IL-13) activation were analyzed further. The H3K4me3 (A) and H4ac (B) marks (counts) upon activation to M(IL-4+IL-13) in the absence (none) or presence of 40 mM NaCl is presented. M(IL-4+IL-13) signature genes analyzed in Figure 1 and Slc6a12 are indicated on each graph. A single technical replicate was generated for each group, which was repeated in 2 independent experiments and then pooled (total of n = 2). (C) Summary of the effect of M(IL-4+IL-13) activation on genes with an increased expression and either a concordant increase (>1.3-fold), no change (nc), or decrease (<0.7-fold) in H3K4me3 and H4ac chromatin marks. The number of genes that were changed (>1.2-fold) upon activation in the presence of an additional 40 mM NaCl is shown. n = 2 (biological). (D) Representative H3K4me3 counts around the promoter region of M(IL-4+IL-13) signature genes Mgl2 and Slamf1, and the tonicity responsive molecule Slc6a12. The total H3K4me3 counts were normalized by library size.