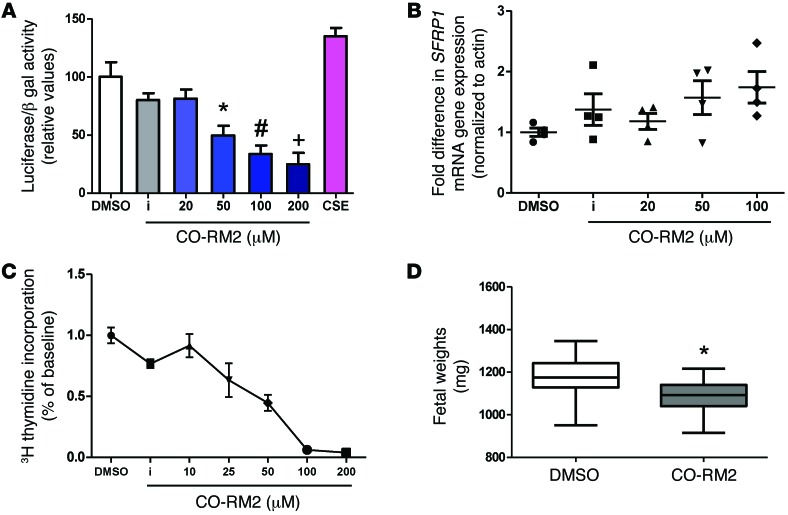
Figure 3. Effect of carbon monoxide analogs on canonical WNT transcriptional activity, sFRP1 expression, trophoblast proliferation, and fetal growth.
(A) Luciferase activity of the canonical WNT reporter in HTR cells transfected with the TOPFLASH TCF reporter plasmid after exposure to varying concentrations of CO-RM2, inactivated CO-RM2 (iCO-RM2), and 10% cigarette smoke extract (CSE) for a period of 24 hours. The normalized value of unstimulated control was arbitrarily set at 100%. Bars represent mean values of 3 different experiments; error bars indicate SEM. P < 0.001 by ANOVA, *P < 0.05 for 50 μM CO-RM2 versus DMSO control by t test, #P < 0.05 for 100 μM CO-RM2 versus control by t test, +P < 0.05 for 200 μM CO-RM2 versus DMSO control by t test. (B) Relative quantification of SFRP1 mRNA levels measured by qRT-PCR in HTR cells after exposure to CO-RM2 for a period of 24 hours. Data are presented as scatter plot (mean ± SEM). SFRP1 expression was increased after exposure to 100 μM CO-RM2 compared with that after exposure to DMSO control (P < 0.05 by t test). (C) Dose-dependent reduction of [3H] thymidine incorporation in serum-starved HTR cells after exposure to varying concentrations of CO-RM2. Inactivated CO-RM2 had no effect of [3H] thymidine incorporation. Experiments were performed twice, in triplicate (mean ± SEM). (D) Fetal weights on E18 were decreased in CD1 pregnant mice injected on E15 with CO-RM2 (n = 5 litters, 63 fetuses) as compared with those injected with 1% DMSO vehicle (n = 5 litters, 67 fetuses). Data are presented as a box plot (25th–75th percentile), with horizontal bars representing median values and whiskers representing minimum and maximum values (*P < 0.001 versus mice injected with DMSO vehicle by t test).