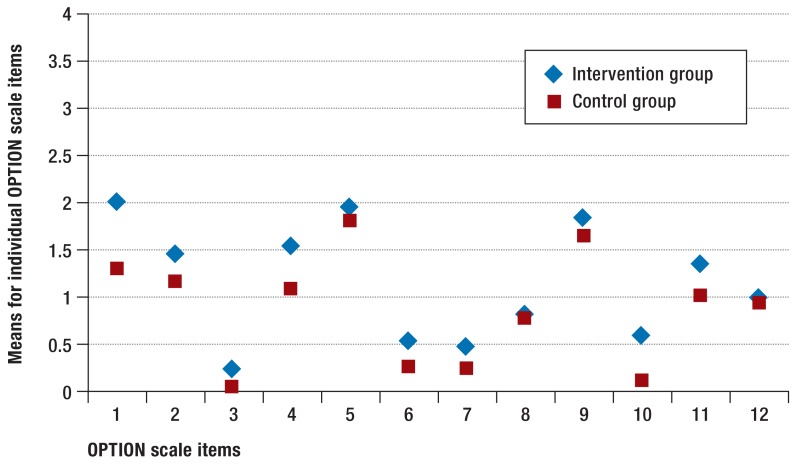
Figure 2.
Means for individual items of the Observing Patient Involvement (OPTION) Scale
1: The clinician draws attention to an identified problem as one that requires a decision making process.
2: The clinician states that there is more than one way to deal with the identified problem (’equipoise’).
3: The clinician assesses patient’s preferred approach to receiving information to assist decision making (e.g. discussion in consultations, read printed material, assess graphical data, use videotapes or other media.
4: The clinician lists ’options’, which can include the choice of ’no action’.
5: The clinician explains the pros and cons of options to the patient (taking ’no action’ is an option).
6: The clinician explores the patient’s expectations (or ideas) about how the problem(s) are to be managed.
7: The clinician explores the patient’s concerns (fears) about how problem(s) are to be managed.
8: The clinician checks that the patient has understood the information.
9: The clinician offers the patient explicit opportunities to ask questions during decision making process.
10: The clinical elicits the patient’s preferred level of involvement in decision making.
11: The clinician indicates the need for a decision making (or deferring) stage.
12: The clinician indicates the need to review the decision (or deferment)