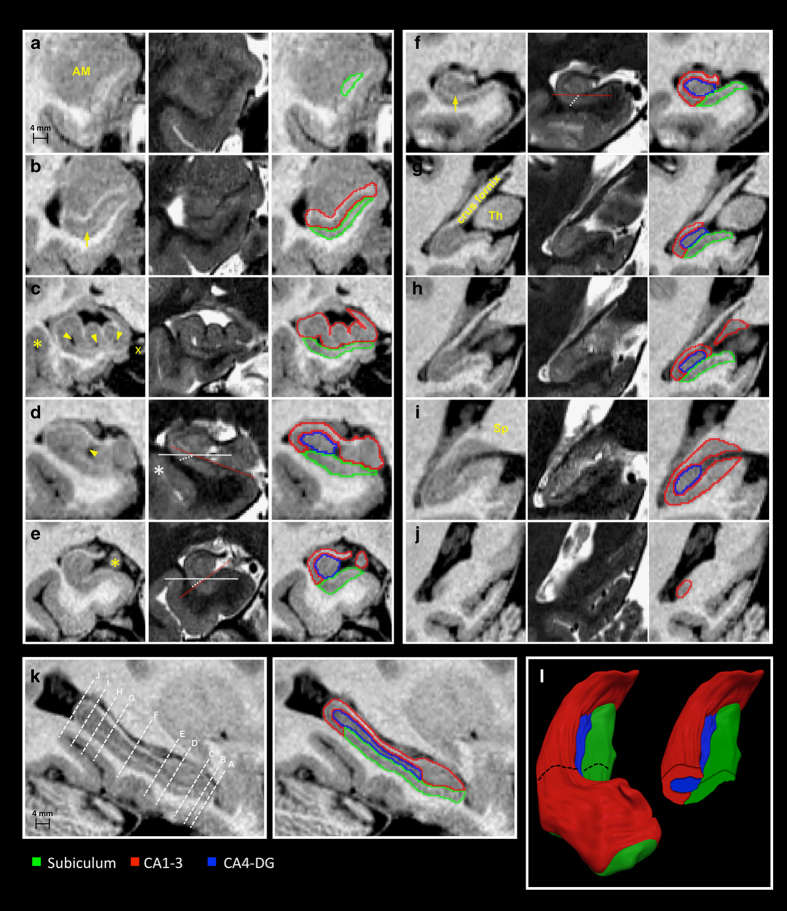
Figure 2. Anatomical boundaries of hippocampal subfileds on T1- and T2-weighted MRI.
Sections displaying critical landmarks are shown. (a,j) are the most rostral and caudal coronal sections. (a) The rostral-most tip of the hippocampus is composed of the subiculum; at this level, the alveus surrounds the subiculum, separating it from the overlying amygdala (AM). (b) When CA1 first becomes visible, it runs parallel to the subiculum; the structures are separated by the subicular molecular layer (arrow). (c) Vertical digitations of CA1-3 (arrowheads point to cavities within the hippocampal sulcus; x indicates the ambient cistern); the supero-lateral subicular interface with CA1 is drawn along a line following the hippocampal sulcus, directed towards the fundus of the collateral sulcus (asterisk). (d) The rostral-most portion of CA4-DG is set at the section where the medial portion of the DG, the margo denticulatus, becomes visible (arrowhead). (e) Junction between head and body, at the level of the uncal apex (asterisk). (f) Hippocampal body; the arrow points to the molecular layer of the subiculum. (g) Rostral portion of hippocampal tail: the crus fornix is fully visible and well demarcated from the thalamus (Th). (h) The caudal slice of the subiculum is set to the posterior-most section on which the thalamus can be identified. (i) Middle segment of the tail. The subiculum is replaced by CA1-3, at the level at which the crus fornix fuses with the splenium (Sp) of the corpus callosum. (j) Terminal segment of the tail. (k) Sagittal hippocampal section displaying planes of the coronal cuts. (l) 3D surface rendering of hippocampal subfields with a coronal cut at the level of the body. On coronal sections, the orientation of the hippocampal body varies across individuals, modifying the spatial relationships between subiculum and CA1. In d, the hippocampus is oriented clockwise. In e, it is oriented counter-clockwise and in f it has a horizontal position. The red line follows the slope of the superior border of the subiculum, the solid white line represents the horizontal axis, and the dashed white line is placed at the boundary between subiculum and CA1.