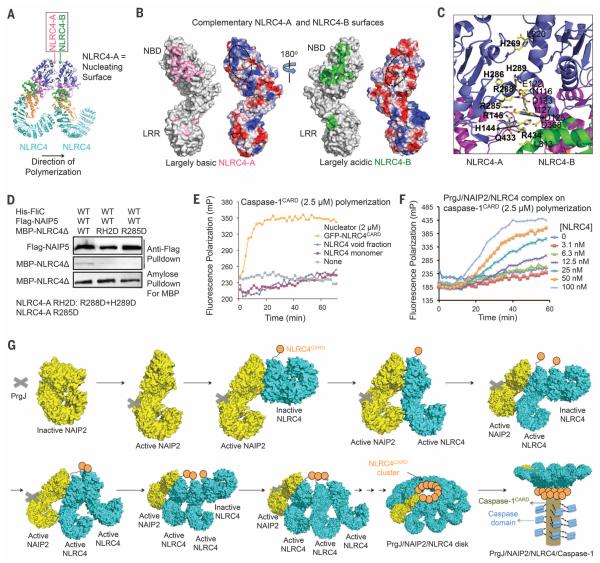
Fig. 4. NLRC4 polymerization and caspase-1 activation.
(A) Locations of NLRC4-A and NLRC4-B surfaces. (B) Mapped interactions at NLRC4-A (pink) and NLRC4-B (green) surfaces and the surface electrostatic potentials. (C) Detailed interactions between two neighboring NLRC4 molecules. Those on the A surface are labeled in boldface. (D) Mutations at the NLRC4-A surface impaired NLRC4 recruitment. Three proteins were coexpressed in 293T cells. The Flag tag was used to pull down the complex; component proteins were detected using Western blots. (E) NLRC4CARD, instead of NLRC4FL, nucleates filament formation of labeled caspase-1CARD, as shown by increase in fluorescence polarization. (F) The PrgJ-NAIP2-NLRC4FL inflammasome nucleates filament formation of labeled caspase-1CARD at substoichiometric ratios, as shown by increase in fluorescence polarization. (G) Schematic diagram for mechanism of PrgJ-NAIP2–nucleated polymerization of NLRC4, followed by caspase-1 dimerization and activation.