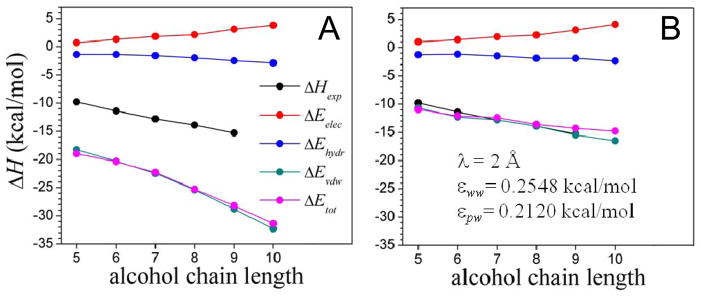
Figure 7.
Energy contributions to the binding energy of the MUP-I protein to a series of aliphatic alcohols as a function of the chain length, calculated with the implicit solvent model (Eelec given by eq 10; Evdw by eq 4, and Ehydr is the cavity-formation energy). (A) Uncorrected dispersion energy ( in eq 4); and (B) solvent-dispersion corrected energy ( ). The structures of the complexes are taken from the PDB; accession codes 1znd, 1zne, 1zng, 1znh, 1znk, 1znl, for pentan-, hexan-, heptan-, octan-, nonan-, and decan-1-ol, respectively. The experimental binding enthalpy26 (ΔHexp) is also shown (ITC data for decan-1-ol not available). Binding is dominated by dispersive forces, as determined by the extent of sub-optimal hydration of the binding pocket.