Fig. 1.
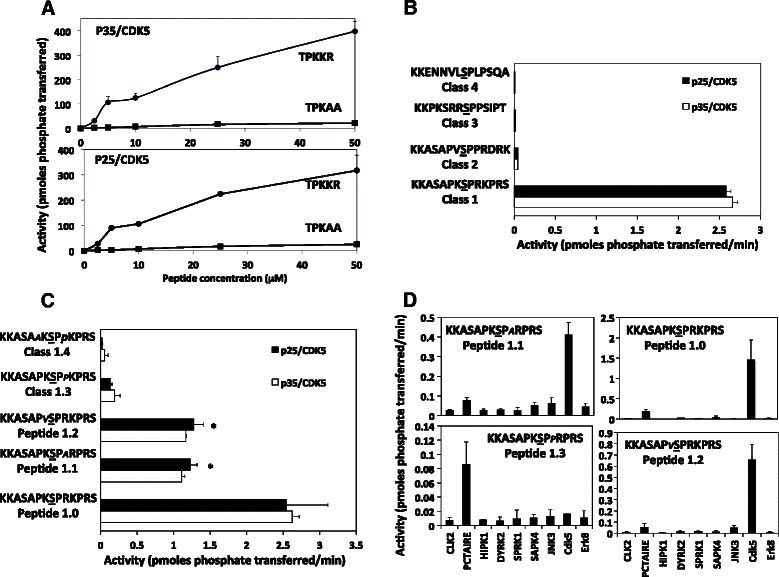
In vitro analysis of primary sequence determinants for p35/CDK5 and p25/CDK5. a The contribution of C-terminal Arg/Lys residues to recognition and phosphorylation by each CDK5 complex was assessed by incubating the peptides at the indicated concentrations with 2 m units of each CDK5 complex for 20 mins and measuring phosphate transferred to each peptide. b Each CDK5 complex was incubated for 20 mins with 100 μM of the indicated peptides representing the primary sequence of the 4 classes of CDK5 substrates. The phosphorylated residue is underlined. c To assess the contribution of specific residues ±2 positions from the target residue a further 4 peptides (at 100 μM) were incubated with 2mUnits of each CDK5 complex for 30 mins. The residue changed from the parent sequence (peptide 1.0) is in italics in each case. *indicates p < 0.05 compared to peptide 1.0. d The rate of phosphorylation of the indicated peptides by several members of the CMGC family of kinases was compared by incubating each peptide (at 50 μM) with 2 m units (as determined against the generic substrate MBP) of each kinase for 30 mins and phosphate transfer measured. In all figures the data is presented as the average of at least two different experiments performed in duplicate ± the SEM, and is given as total picomoles transferred during the assay (a) or pmoles transferred/min (b-d)
