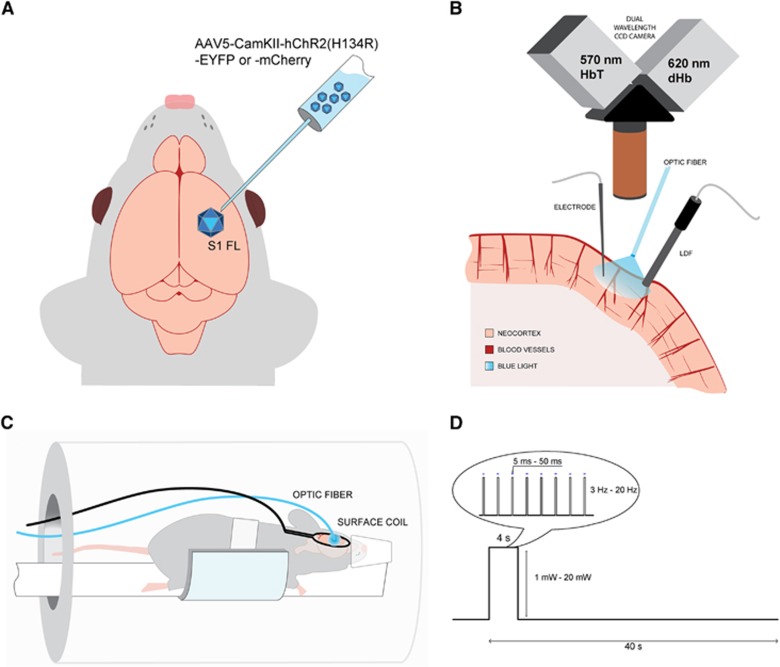
Figure 1.
Experimental setup. (A) Adeno-associated virus expressing channelrhodopsin (ChR2) conjugated with YFP or mCherry was transduced in rat forelimb primary somatosensory cortex (S1FL). Follow-up studies were performed 3 to 4 weeks after inoculation. (B) For optical studies, the brain at the ChR2 expression site was exposed, and a multimode optic fiber with 400-μm core diameter was positioned for stimulation of ChR2 with blue laser. Dual wavelength hemoglobin-weighted optical intrinsic signal (OIS) was collected at 570-nm isosbestic point, representative of the total hemoglobin (HbT); and at 620 nm, weighted toward deoxyhemoglobin (dHb). Simultaneously, we also performed laser Doppler flowmetry (LDF) for cerebral blood flow measurements. For a subset of the animals, a single electrode was penetrated at the stimulation area to record electrical activity. (C) In the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) setup, a surface coil was positioned on the animal head over the implanted optic fiber and the animal was imaged on a 9.4-T magnetic resonance (MR) system. (D) The block design of the stimulus consisted of 4- second stimulation and 36- second control period. The light pulse duration, power, and frequency were varied and a total of 11 combinations were used for stimulus modulation.