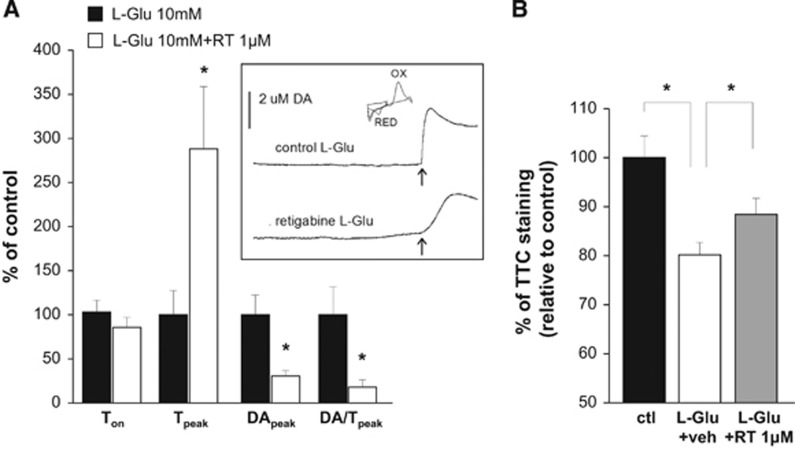
Figure 4.
Effects of retigabine on L-glutamate-induced dopamine release and toxicity. (A) Fast cyclic voltammetry (FCV) experiments showing the effects of 1 μmol/L retigabine on time to onset, time to peak, maximum extracellular dopamine concentration, and mean rate of dopamine efflux in brain slices exposed to 10 mmol/L L-glutamate. Data are expressed as percentage of DMSO-treated slices (controls, black columns). Values are mean±s.e.m. of 5 to 9 slices from 5 to 6 rats. *P<0.05. The inset shows representative experiments of dopamine efflux elicited by oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD) in the presence of vehicle (top trace) and 1 μmol/L retigabine (bottom trace); the arrow indicates the onset of dopamine peak. The cyclic voltammogram generated by plotting the faradaic current against the input voltage is also shown. Peaks due to the oxidation (OX) and reduction (RED) of dopamine are indicated. (B) Bar graph showing the effects of exposure to 10 mmol/L L-glutamate in the presence of DMSO (white column) or 1 μmol/L retigabine (gray column). Data are expressed as percentage of DMSO-treated slices (control with no L-glutamate, black column). Values are mean±s.e.m. of 6 to 8 slices from 3 to 4 rats. *P<0.05.