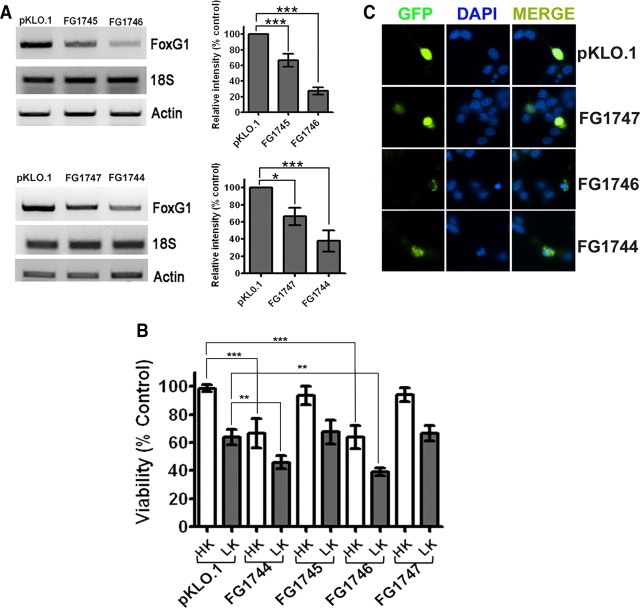
Figure 3.
Suppression of FoxG1 expression promotes neuronal death. CGN cultures were cotransfected with plasmids expressing GFP and either pKLO.1 or one of the four different FoxG1 shRNAs (FG1744, FG1745, FG1746, and FG1747). The ability of the shRNAs to suppress FoxG1 expression was evaluated in HT22 cells, and their effect on neuronal survival was analyzed in CGNs. A, RNA was extracted from HT22 cells 72 h after transfection with shRNA constructs and subjected to RT-PCR analysis using primers against FoxG1, 18S ribosomal RNA, and actin. Results for the four FoxG1 shRNAs [FG1745 and FG1746 (upper panel) and FG1747 and FG1744 (lower panel)] along with the control (pKLO.1) are shown. Densitometric analysis of the FoxG1 band from three separate experiments was performed using Kodak 1D software, and the results are shown in the graph. ***p < 0.001, *p < 0.05. For statistical analysis, one-way ANOVA was performed using Bonferroni's multiple-comparison test. B, CGNs were cotransfected with plasmids expressing GFP and pKLO.1 or one of the four FoxG1 shRNAs and treated with HK or LK medium. Results come from three separate experiments performed in duplicate. ***p < 0.001 as compared to neurons cotransfected with GFP and pKLO.1 in HK. **p < 0.01 as compared to neurons cotransfected with GFP and pKLO.1 in LK. C, Appearance of neurons transfected with pKLO.1 plasmid or FoxG1 shRNA (FG1747, FG1746, FG1744). Transfected neurons were identified by GFP immunocytochemistry and nuclei stained with DAPI.