Figure 4.
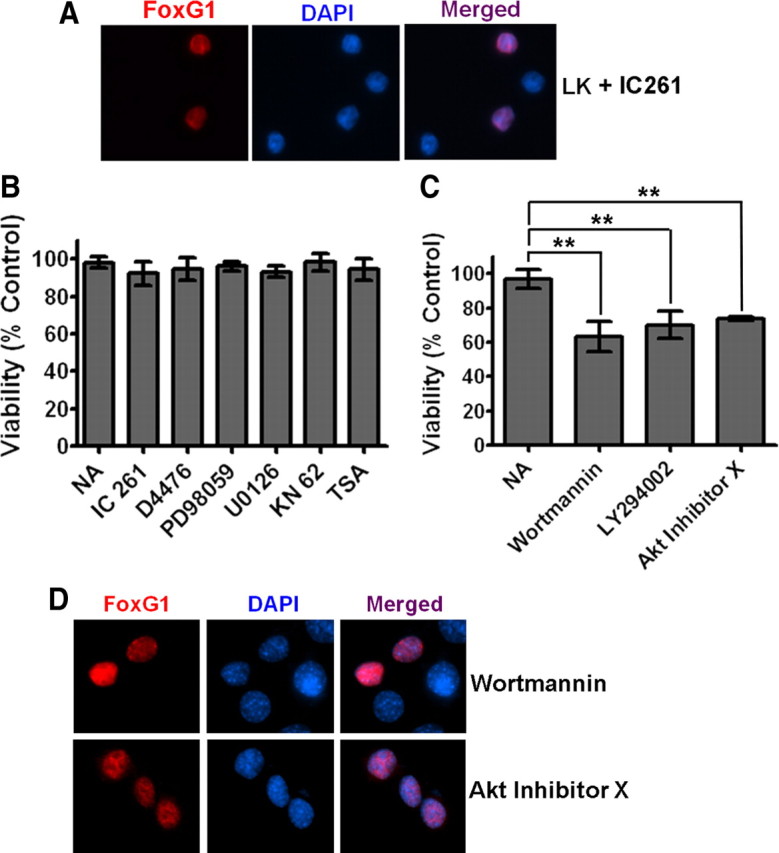
The PI-3 kinase/Akt pathway mediates the anti-apoptotic effect of FoxG1. A, Ectopically expressed FoxG1 was detected immunocytochemically with a Flag antibody and nuclei were stained with DAPI. The figure shows nuclear localization of FoxG1 in neurons treated with LK in presence of IC261. CKI inhibition does not alter the nuclear localization of FoxG1. B, CGN cultures transfected with Flag-FoxG1 were switched to LK medium having no additives (NA), LK medium containing 10 μm IC261, 10 μm D4476, 40 μm PD98059, 10 μm U0126, 50 μm KN62, or 1 μm trichostatin A. The survival status of transfected neurons was quantified 24 h later by Flag immunocytochemistry and DAPI nuclear staining. Inhibitors against CKI, CaMK, HDACs, and the RAf-MEK-ERK pathway did not have any effect on FoxG1-mediated survival. Results were obtained from three independent experiments performed in duplicate. Control experiments (supplemental Table 1, available at www.jneurosci.org as supplemental material) confirmed that all the pharmacological agents used in this analysis inhibit the activities of their targets. C, CGN cultures transfected with Flag-FoxG1 were switched to LK medium with NA or LK medium containing 200 nm wortmannin, 20 μm LY294002, and 5 μm Akt inhibitor X. Inhibitors of the PI-3 kinase/Akt pathway blocked FoxG1 from helping CGNs to survive in LK conditions. **p < 0.01 as compared to FoxG1-transfected CGNs treated with LK. Results were obtained from three independent experiments performed in duplicates. D, HT22 cells were transfected with Flag-FoxG1. Six hours after transfection, the medium was changed to fresh medium supplemented with 200 nm wortmannin or 5 μm Akt inhibitor X for 12 h. Immunocytochemistry was performed with Flag antibody and nuclei were stained with DAPI. Blocking PI3K/Akt does not block nuclear translocation of FoxG1.
