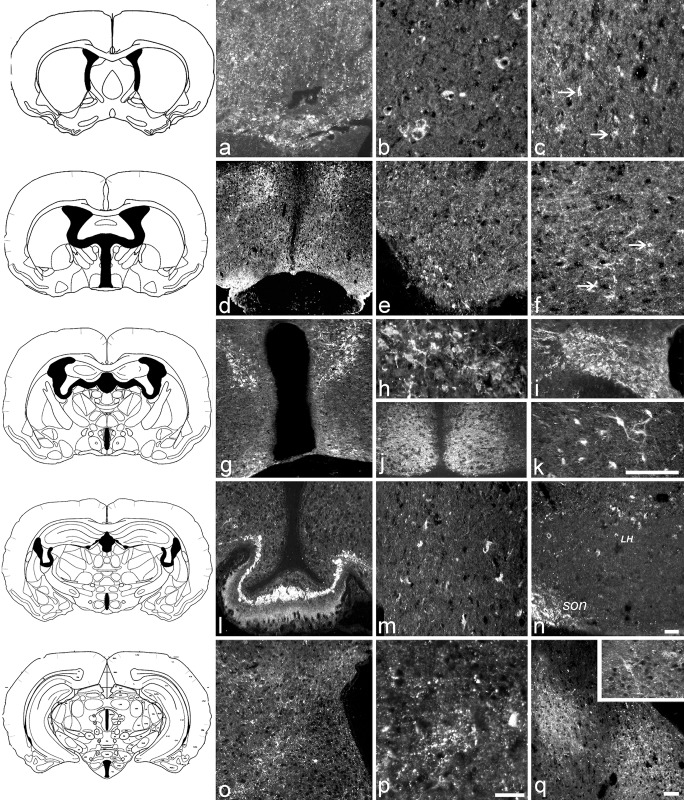
Fig 3. VGF C-/N- terminus peptide localization in the hamster brain.
According to Morin and Wood, 2001 [36] coronal sections were stained at the level of (top to bottom) OVLT including area (a, b, c), preoptic area (d, e, f), supraoptic region (g, h, i, j, k), median eminence (ME, l, m, n) and arcuate nucleus (o, p, q, insert). VGF peptides are found in small axons and a number of nerve terminals of OVLT (a, C-terminus), and in the brain cortex within single punctuate cell bodies (b, N- terminus, frontal; c, C-terminus, parietal; arrows indicate small perikarya) as well as axons labelled by the VGF C-terminus only (c, C-terminus, parietal). Within the preoptic area, labelling was seen in the entire MPN (d, low magnification; C-terminus), within widely distributed axons and nerve terminals (e, f: C- and N- terminus, respectively), and small scattered perikarya (f, N- terminus arrows indicate the small perikarya). In the supraoptic region, labelling was abundant in many nuclei (g, low magnification, C- terminus) including Pa (h, C-terminus), SON (i, C- terminus) and SCN (j, N-terminus). In the same section, hippocampus CA3 (k, C- terminus) was rich in positive perikarya. ME (l, C- terminus) was labelled more intensively in the internal than in external layer, with Herring bodies brightly labelled. Perikarya were also visible in DM nucleus (m, C- terminus) and in an area just underneath the SON hence may compatible with LH (n, C- terminus). Immunopositive axons and nerve terminals (o, p; C- and N- terminus, respectively) were also found through the entire actuate nucleus and in amygdaloidei nuclei (q, C-terminus), in which scattered cell bodies were also visible (q, insert). Scale bars: a, c, f, m, p:100 μm; e, j, o, q: 100 μm; d, g, l, n: 200 μm; b, h, i, k, insert:100μm. SON: supraoptic nucleus, LH: lateral hypothalamic area.