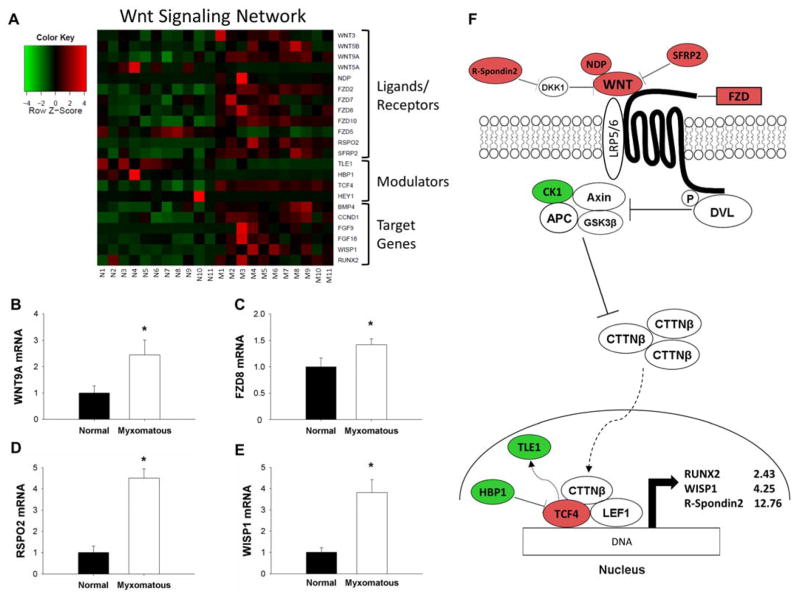
Figure 3. Changes in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling in MMVD.
A) Heat map of differentially expressed canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling-related genes in myxomatous (columns M1–M11) versus non-myxomatous (columns N1–N11) human mitral valves. Red = increased expression, green = reduced expression. B–E) qRT-PCR confirmation of differential gene expression of Wnt9a ligand (B), FZD8 receptor (C), R-spondin 2 (D) and WISP1 (E) in myxomatous versus non-myxomatous mitral valves (n = 11 non-myxomatous valves, n = 10 myxomatous valves;* = p<0.05). qRT-PCR experiments were performed on the same samples of human mitral valve tissue used for microarray analyses. F) For ease of reference, a simplified working model of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling in MMVD (color coding as for Panel 3A). For clarity, non-myxomatous control valves are referred to as “normal”. APC = Adenomatous polyposis coli; AXIN = Axis inhibition protein; BMP4 = bone morphogenetic protein 4; CK1 = Casein kinase 1, alpha 1; CTTNβ = Beta-catenin; DKK1 = Dickkopf 1 (Xenopus laevis); DVL = Dishevelled; FGF = fibroblast growth factor; FZD = Frizzled family receptor; HBP1 = HMG-box transcription factor 1; LEF1 = Lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1; NDP = Norrie disease (pseudoglioma); RSPO2 = R-spondin 2; RUNX2 = Runt-related transcription factor 2; SFRP2 = Secreted frizzled-related protein 2; TCF4 = Transcription factor ; TLE1 = Transducin-like enhancer of split 1; WISP1 = Wnt-inducible signaling pathway protein 1; WNT = Wingless-type MMTV integration site family.