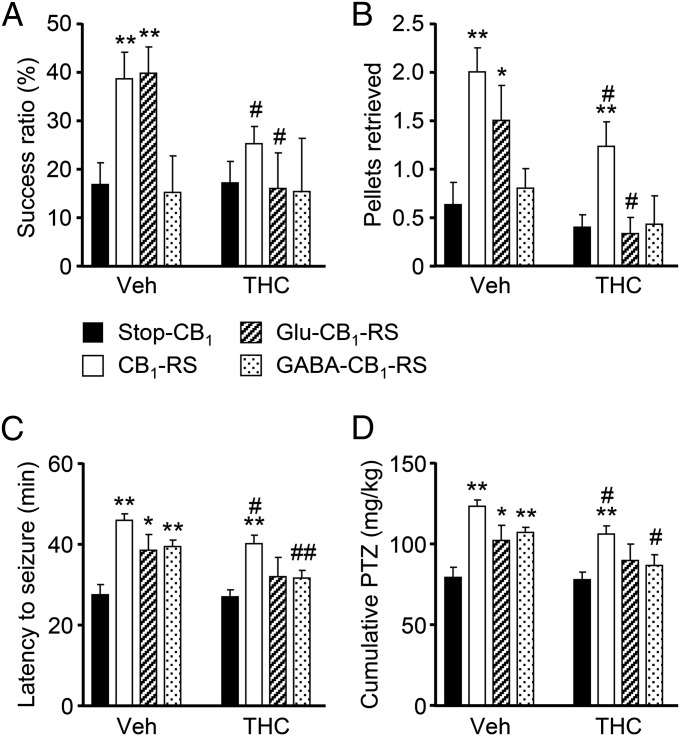
Fig. 5.
Selective CB1R expression rescue restores functional alterations and reestablishes THC susceptibility in Stop-CB1 mice. (A and B) Skilled motor activity was assessed by the skilled pellet-reaching (A) and staircase (B) tests in adult CB1R-rescued mice [n = 15 and 15 (Stop-CB1 vehicle- and THC-treated mice, respectively); n = 20 and 17 (CB1-RS vehicle- and THC-treated mice, respectively); n = 9 and 6 (Glu-CB1-RS vehicle- and THC-treated mice, respectively); n = 5 and 7 (GABA-CB1-RS vehicle- and THC-treated mice, respectively)]. (C and D) Seizure susceptibility to subconvulsive doses of PTZ was determined. Latency to seizures (C) and the cumulative dose of PTZ required (D) are shown [n = 13 and 19 (Stop-CB1 vehicle- and THC-treated mice, respectively); n = 18 and 19 (CB1-RS vehicle- and THC-treated mice, respectively); n = 9 and 5 (Glu-CB1-RS vehicle- and THC-treated mice, respectively); n = 9 and 8 (GABA-CB1-RS vehicle- and THC-treated mice, respectively)]. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. corresponding Stop-CB1 mice; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. corresponding vehicle-treated group.