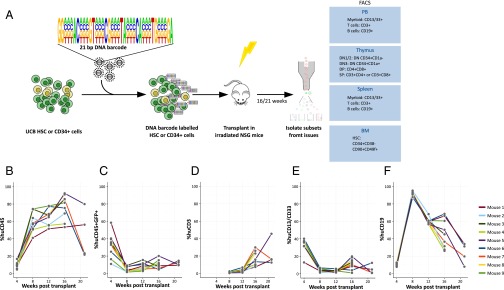
Fig. 1.
Barcoding human HSC and xenotransplantation. (A) Human HSC (CD34+CD38−CD45RA−CD90+CD49f+) or CD34+ cells were isolated and transduced with the PTGZ barcode library carrying 21 variable bases in the barcode with a total complexity of 485 different barcodes. The transduced cells were transplanted in to 5- to 6-wk-old sublethally irradiated NSG mice. The mice were bled monthly and myeloid cells, T cells, and B cells were isolated from PB. At 16 or 21 wk, the experiment was terminated and, in addition to PB, cells isolated from thymus, spleen, and BM were sorted as indicated and the barcode content of the samples was analyzed. From the thymus, DN, DP, and SP cells were isolated using the indicated markers. Chimerism in the PB of nine mice transplanted with 1,000 purified human HSCs as determined by human CD45 expression (B) and GFP marking of human cells (C). Development of CD3+ T cells (D), CD13+/CD33+ myeloid cells (E), and CD19+ B cells (F) within the human CD45+ population were followed in time after transplantation of the transduced cells.