Fig. 5.
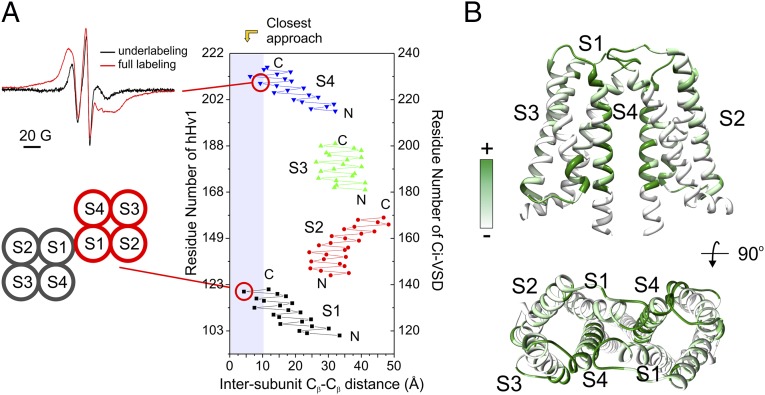
The hHv1-VSD dimer interface agrees with CiVSD-WT dimer structure. (A) (Upper Left) Strong dipolar coupling from spin-labeled hHv1-VSD-206C. (Lower Left) Mutant 121C at top of S1 can form spontaneous disulfide linkage in native hHv1 (38). (Right) Cβ distances between hHv1 monomer according to the CiVSD-WT dimer (PDB ID code 4G80). Both residues 121 and 206 are among the closest residues (<10 Å). (B) hHv1-VSD dimer model built by aligning two monomer structural models with CiVSD-WT dimer crystal structure. The cross-linking data from mHv was mapped onto the dimer model (40), and regions with high cross-linking propensities, including S4 and top of S1, are in close proximity in the dimer model.