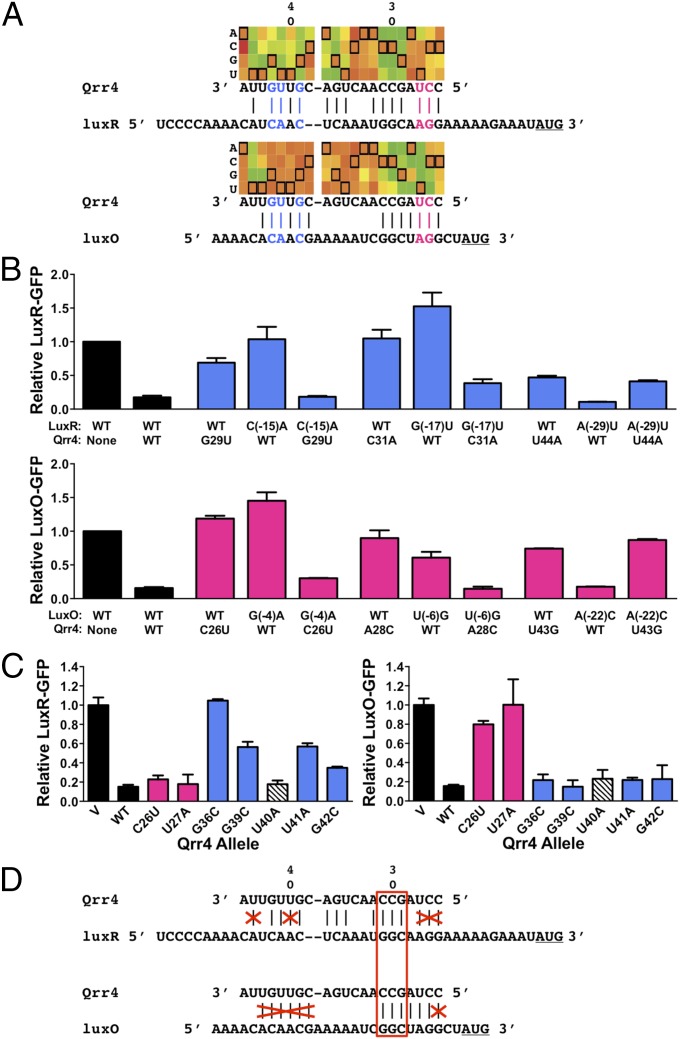
Fig. 6.
Qrr4 mutations can block base pairing. (A) Region of heat map showing results of RSort-Seq analysis for regulation of luxR and luxO in the putative base-pairing region, the corresponding Qrr4 sequence, and the aligned target mRNA 5′-UTR sequence. See Fig. 2 for explanations of nomenclature and colors. RSort-Seq predicts Qrr4 bases used to regulate only luxR (blue) or only luxO (pink). (B) WT and mutant Qrr4 regulation of luxR-gfp (Upper, blue) or luxO-gfp (Lower, pink) in E. coli. (C) Comparison of the ability of WT and Qrr4 mutants to repress luxR and luxO. Blue bars show nucleotides essential for luxR regulation, pink bars show nucleotides essential for luxO regulation, and the white hatched bar shows that Qrr4-U40 is not required for regulation of luxR or luxO. (D) Model for predicted and actual critical base pairing between Qrr4 and luxR and Qrr4 and luxO. Bases crossed out in red represent nucleotides that have the potential to base pair but that are not important for regulation of the given target. The red box shows the only 3 nucleotides required for base pairing to and regulation of both targets. In all panels, error bars are SDs of at least three trials.