Fig. 4.
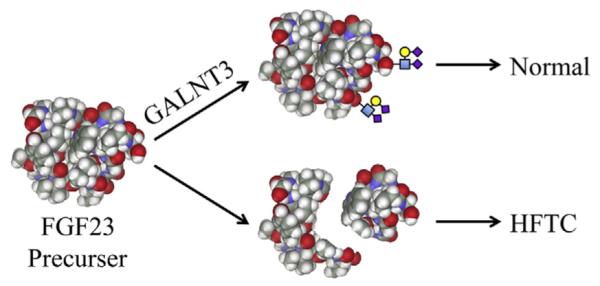
Mechanism for GALNT3 mutations causing hyperphosphatemic familial tumoral calcinosis (HFTC). HFTC can be caused by mutations in GALNT3, FGF23, or KL (FGF23 receptor klotho). GALNT3 is a Golgi enzyme that is required for the O-glycosylation of FGF23. Glycosylation of FGF23 protects it from proteolytic inactivation that results in elevated serum phosphate (causing HFTC).
