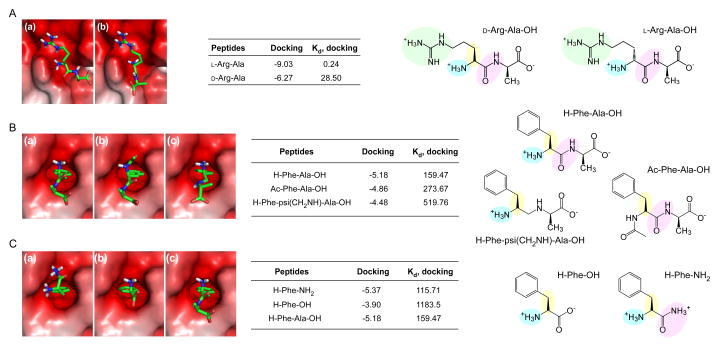
Figure 2.
Interaction between N-recognins and N-end rule pathway inhibitors (A) Binding modes calculated through in silico docking analysis of (a) L-Arg-Ala and (b) D-Arg-Ala with the UBR1 box (Protein Data Bank [PDB] code: 3NY3), and binding affinities (kcal/mol) and dissociation constants (μM) of the docked complexes. (B) Binding modes, binding affinities (kcal/mol), and dissociation constants (μM) of (a) Phe-Ala, (b) Ac-Phe-Ala, and (c) Phe-psi(CH2NH)-Ala with the ClpS domain (PDB code: 3DNJ). (C) Same as (B), except that Phe and its derivatives are used for the in silico docking analysis. Positively charged side chains, e.g., guanidino groups in Arg for interaction with the UBR box, are shown in green spheres in the chemical structures. Essential components of small molecules for interaction with UBR proteins, such as L-conformation, protonated α-amine groups, and amide bond characters, are shown in yellow, blue, and pink spheres, respectively.