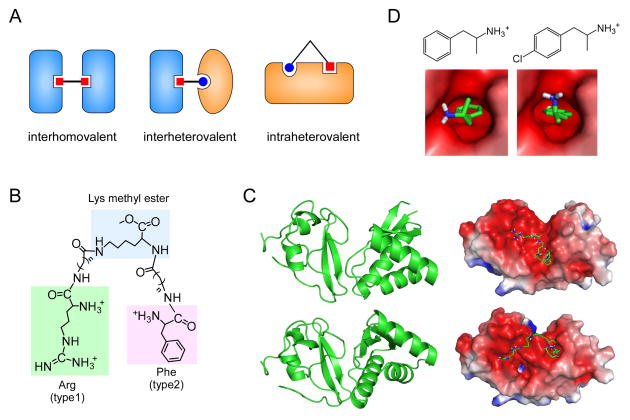
Figure 3.
Multivalent and monovalent inhibitors of the N-end rule pathway. (A) Types of multivalent ligands bound to their cognate proteins. (B) Structures of heterovalent molecule RF-Cn (where n indicates the length of hydrocarbon chains) tethering the core Lys methyl ester to the N-terminal Arg (type 1 destabilizing residue) and Phe (type 2), which are indicated by green and pink backgrounds, respectively. (C) Two possible structures of the UBR box-N-domain “combined” proteins (left) and their binding modes with the RF-C5 compound (right). Protein structures and docking models were obtained by using the Gramm-X protein-protein docking web server and semi-empirical PM6 method with the Gaussian 09 program [30]. (D) Chemical structures of amphetamine (left) and para-chloroamphetamine (right), and their binding modes with the N-domain (PDB code: 3DNJ) calculated with a ligand-receptor docking computation by using AutoDock version 4.2 with the Lamarckian genetic algorithm [85].