Fig. 1.
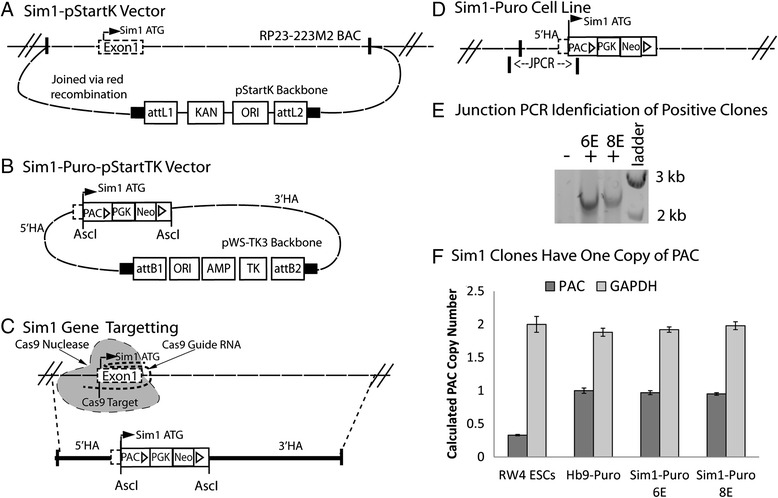
Generation and identification of Sim1-Puro cell line. a Red recombineering was utilized to insert the region approximately 2 kb upstream to 10 kb downstream of Exon 1 of the Sim1 gene from RP23-223 M2 BAC into the pStartK backbone, generating the Sim1-pStartK plasmid. b After AscI cut sites were introduced by another red recombination reaction, a PAC-PGK-Neo cassette was inserted into the open reading frame of Sim1 Exon1in the Sim1-pStartK plasmid. Using gateway recombination, the pStartK backbone was replaced with the pWS-TK3 backbone to introduce the negative selection gene, TK. 5’ and 3’ homology arms are labeled. c CRISPR/Cas9 targeting of the Sim1 gene was used to generate a double stranded break at the desired recombination location. Sim1-Puro-pStartTK recombined into the Sim1 locus as shown by the dotted lines. 5’ and 3’ homology arms are labeled. d The Sim1-Puro cell line with PAC in Sim1 Exon 1. Junction PCR (JPCR) primer for approximately 2.6 kb was used to screen for the desired recombination event. e JPCR bands of positive (+) and negative (−) clones with a 1 kb ladder. f Copy number assay shows Sim1 clones have one copy of PAC by comparison with RW4 ESCs (0 copy) and Hb9-Puro ESC (1 copy) controls. AMP, Ampicillin resistance gene; AscI, Restriction enzyme site; attB1 & attB2, Gateway recombination results; HA, Homology arm; JPCR, Junction PCR; ori, Origin of replication; PAC, Puromycin resistance gene; PGK, Phosphoglycerate kinase promoter sequence; Neo, Neomycin resistance gene; Sim1 ATG, Translation start in Sim1 Exon1; TK, Thymidine kinase
