FIGURE 1.
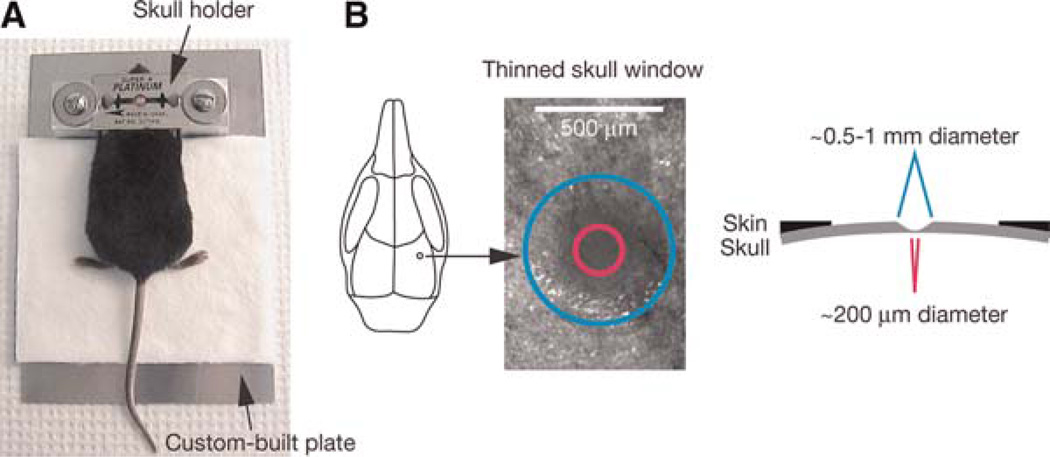
Schematic of thinned skull preparation. A head immobilization device including a custom-built plate and a skull holder is used for reducing movement artifacts during imaging (A). The skull holder/razor blades are glued onto the mouse skull such that the region of interest is exposed in the center of the circular hole of the razor blades. The skull holder/razor blades are then tightened on the aluminum blocks of the custom-built plate. A circular area of skull (typically ~0.5–1mm in diameter, marked with a blue circle) over the region of interest is shaved (B). The thinnest region (marked with a pink circle) for TPLSM imaging is ~20 µm in thickness and ~200 µm in diameter.
FIGURE 1.
Schematic of thinned skull preparation. A head immobilization device including a custom-built plate and a skull holder is used for reducing movement artifacts during imaging (A). The skull holder/razor blades are glued onto the mouse skull such that the region of interest is exposed in the center of the circular hole of the razor blades. The skull holder/razor blades are then tightened on the aluminum blocks of the custom-built plate. A circular area of skull (typically ~0.5–1mm in diameter, marked with a blue circle) over the region of interest is shaved (B). The thinnest region (marked with a pink circle) for TPLSM imaging is ~20 µm in thickness and ~200 µm in diameter.