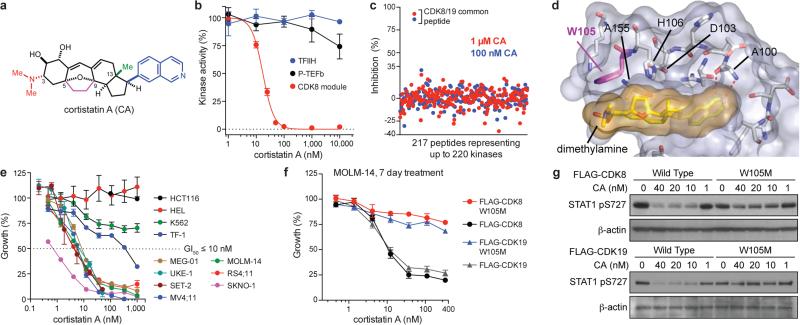
Figure 2. CA suppresses AML cell proliferation by inhibiting Mediator kinases.
(a) CA structure with N,N-dimethylamine red, C5–C9 ethano bridge magenta, C13-methyl green and isoquinoline blue. (b) Phosphorylation of the RNA pol II C-terminal domain (mean ± s.e.m., n=3 biological replicates, one of two experiments shown, autorad in Supplementary Figure 1). (c) Kinome profiling in MOLM-14 lysate (mean, n=2 biological replicates, experiment performed once, values < 35% indicate no change). (d) CA binding pocket of CDK8 from CA-CDK8-CCNC crystal structure (semi-transparent surface; CA in gold, CDK8 in grey) with contact residues and CA in stick representation. Dotted red lines indicate H-bonds. (e) Effect of CA on growth of indicated cell lines (mean ± s.e.m., n=3 biological replicates, one of two experiments shown). (f) Sensitivity of MOLM-14 cells to CA upon expression of indicated kinases (mean ± s.e.m., n=3 biological replicates, one of two experiments shown). (g) Immunoblot showing IFN-γ-stimulated STAT1 S727 phosphorylation in MOLM-14 cells expressing indicated kinases and treated with CA (one of two experiments shown, full scan in Supplementary Figure 1).