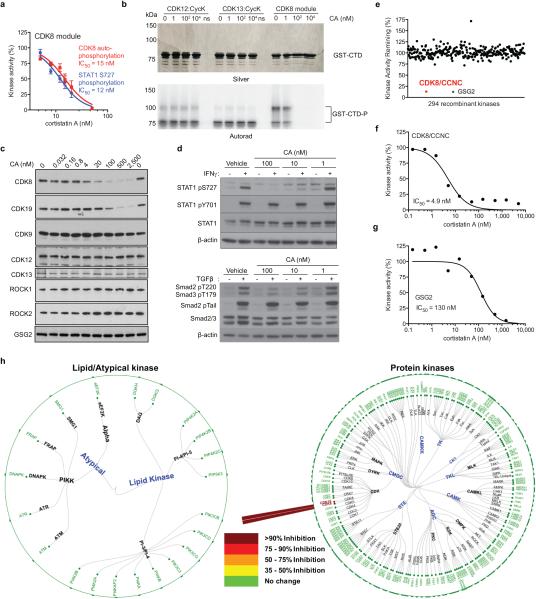
Extended Data Figure 2. CA inhibition of and binding to CDK8.
(a) CA inhibition of CDK8 module phosphorylation of CDK8 and STAT1 S727 substrate (mean ± s.e.m., n=3 biological replicates, one of two experiments shown, autorad in Supplementary Figure 1). (b) CA inhibition in vitro of CDK8 module activity but not CDK12:Cyclin K or CDK13:Cyclin K activity up to 10 μM. Equal amounts (silver stain) of GST-CTD were used as the substrate in in vitro kinase assays. The amount of each kinase used was empirically determined to give approximately the same GST-CTD signal under the assay conditions. “ns” is no substrate (kinase only) and “GST-CTD-P” is phosphorylated GST-CTD. One of four experiments shown. (c) Immunoblot showing that CA selectively and dose-dependently inhibits capture of native CDK8 (IC50 ~10 nM) and CDK19 (IC50 ~ 100 nM) from MOLM-14 lysates but did not inhibit capture of CDK9, CDK12, CDK13, ROCK1, ROCK2 or GSG2. One of two experiments shown, full scan in Supplementary Figure 1. (d) Immunoblots showing CA inhibition of CDK8-dependent IFN-γ-stimulated STAT1 S727 phosphorylation in MOLM-14 cells and CA inhibition of TGF-β-stimulated Smad2 T220 and Smad3 T179 phosphorylation in HaCaT cells (IC50 < 100 nM). One of two experiments shown, full scan in Supplementary Figure 1. (e) In vitro kinase activity profiling (mean for kinase reaction, n=2 biological replicates, experiment performed once). (f,g) CA dose-dependent inhibition of (f) CDK8/CCNC complex (IC50 = 5 nM) and (g) GSG2 (IC50 = 130 nM) as measured for the (e) (n=1, experiment performed once). (h) Dendrogram representation of results shown in Fig. 2c for 1 μM CA.