Figure 2. Characterization of pAzF-261-A488.
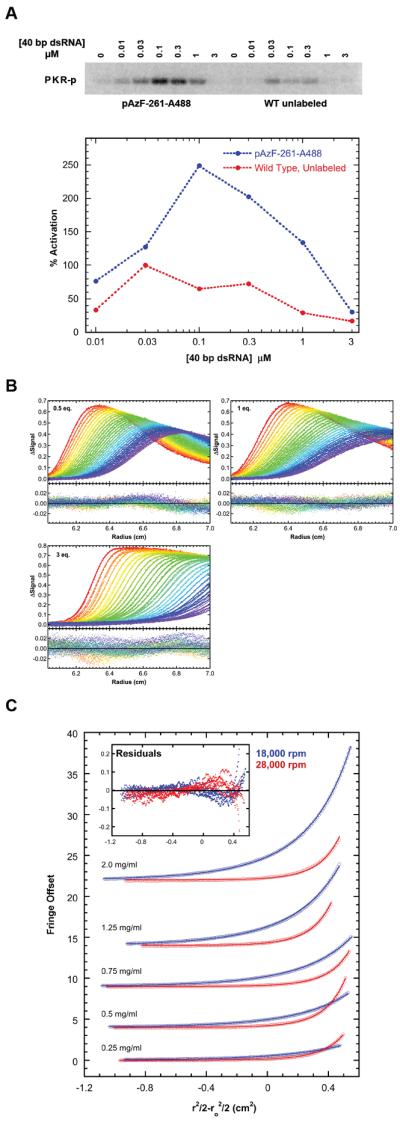
(A) Activation of pAzF-261-A488 by 40 bp dsRNA. Top: Phosphorimager analysis of wild type, unlabeled PKR (red) and pAzF-261-A488 (blue) activation. Bottom: quantitation. Data were normalized to wild type, unlabeled PKR at 30 nM 40 bp. (B) Sedimentation velocity analysis of pAzF-261-A488 binding to 0.75 μM 40 bp dsRNA. Global analysis of difference curves for at three concentrations of pAzF-261-A488 fit to a 2:1 binding model provides best-fit dissociation constants of Kd1= 0.324 (0.280, 0.376) μM and Kd2 = 0.517 (0.448, 0.579) μM with RMSD = 0.0060 OD. The top panels contain the data (points) and fits (lines) and the bottom panels contain the residuals. (C) Sedimentation equilibrium analysis of pAzF-261-A488 self-association. Global analysis of 5 concentrations and two rotor speeds (18000 rpm – blue, 28000 rpm – red) to a monomer-dimer model results in Kd = 94 (85, 103) μM with RMSD = 0.0327 fringes.
