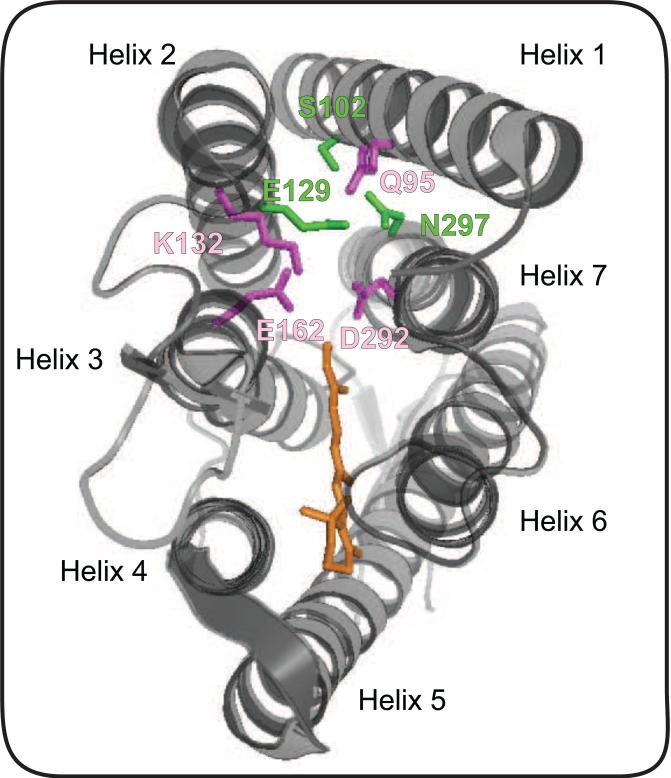
Figure 2. Residues that affect ion selectivity in the channelrhodopsin C1C2.
The illustration shows crystal structure of C1C2, with putative ion gating residues S102, E129 and N297 highlighted in green. Mutation of the gating residue N297 to D results in a significant increase in selectivity for Ca2+, while mutation of E129 to Q or A results in a significant decrease in the channel's Ca2+ selectivity [20]. Mutating the highly conserved gating residue E129 [45] has significant effects on the channel's selectivity for Cl− in both the C1C2 backbone and the ChR2 backbone (position E90 in the ChR2 backbone) [36,37]. Mutation of E90 in ChR2 to R or K increases the reversal potential as a result of increased Cl− selectivity to generate a light activated inhibitory channel [37]. Residues outside of the putative ion gate also influence channel selectivity (residues highlighted in purple). Mutations Q95A, E162 and D292A have all been shown to enhance H+ selectivity. Mutants K132A and Q95A display increased K+ permeability in the C1C2 backbone [20].