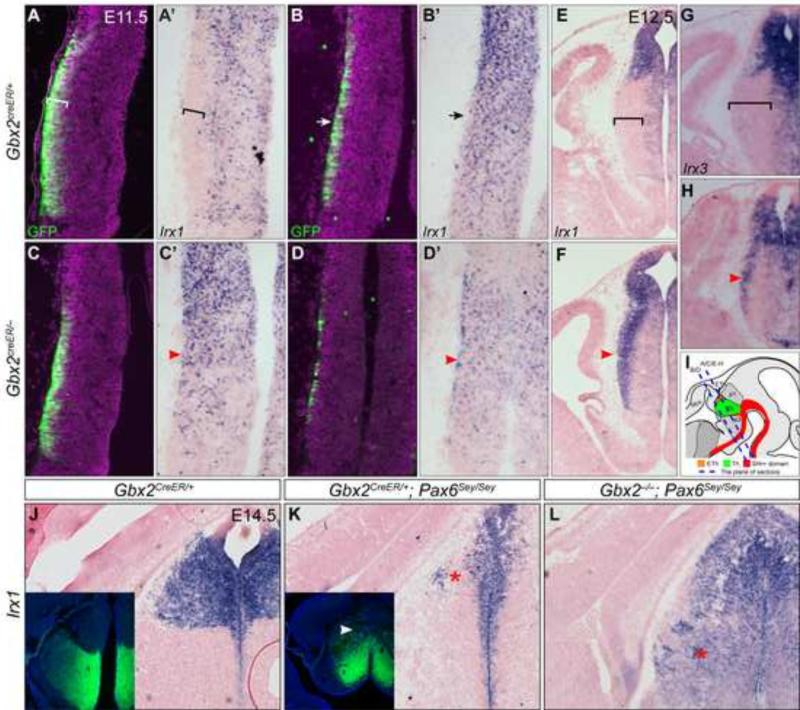
Figure 2. Gbx2 represses Irx genes in postmitotic thalamic neurons.
(A-F) Immunofluorescence and in situ hybridization on coronal sections of control and Gbx2-KO embryos at E11.5 (A-D') and E12.5 (E-H). Antibodies and probes are indicated at the lower left corner; genotypes to the left. (I) Illustration of mouse embryonic brain and the sectioning planes corresponding to A-H. Brackets indicate the GFP/Gbx2 positive and Irx negative domain; arrows show fewer GFP+ cells and remnants of Irx1 transcripts in the anterior part of the thalamus; arrowheads denote the persistent Irx transcripts. (J-L) In situ hybridization for Irx1 on coronal sections of E14.5 brain. Insets show immunostaining for GFP on adjacent sections to J and K respectively. The arrowhead indicates GFP expression in the presumptive habenula; asterisks show the loss (K) or gain (L) of Irx1 expression, respectively.