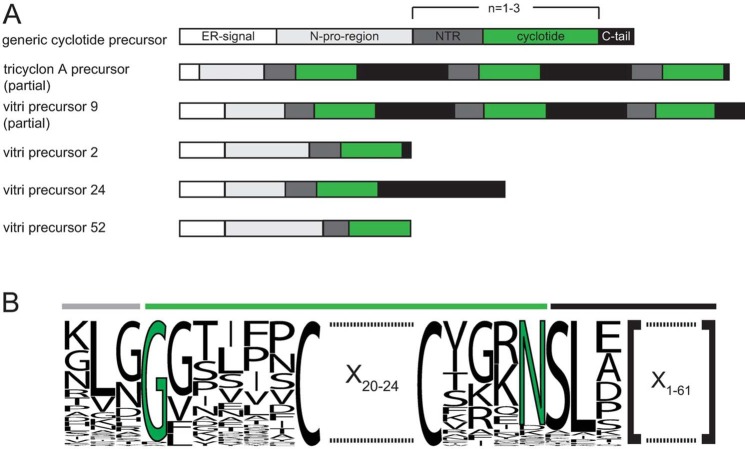
Figure 1.
Viola tricolor cyclotide precursor analysis. (A) A generic cyclotide precursor is ribosomally synthesized and contains an ER signal, followed by a N-pro-region, N-terminal repeats (NTR), the cyclotide domain, and a C-terminal tail region. Cyclotide precursors may encode up to three peptide domains as it has been demonstrated for the V. tricolor tricyclon A precursor. Novel vitri precursors discovered by transcriptome mining contain one, two, or three cyclotide domains. Exemplarily shown are vitri precursors 2 and 9. As indicated each precursor domain may vary in length. For instance, vitri precursor 24 comprises an extended C-tail, whereas vitri precursor 52 completely lacks this domain. (B) Sequence comparison of vitri precursor processing site has been provided by a sequence logo. Three adjacent residues downstream of the C-terminus of the mature cyclotide domain in positions P′1, P′2, and P′3, and upstream of the N-terminus of the mature cyclotide domain in positions P1, P2, and P3 have been considered for being essential for precursor processing and cyclization in planta. Loop six comprises the highly conserved ligation sites, namely, glycine and asparagine or aspartic acid as highlighted in green.