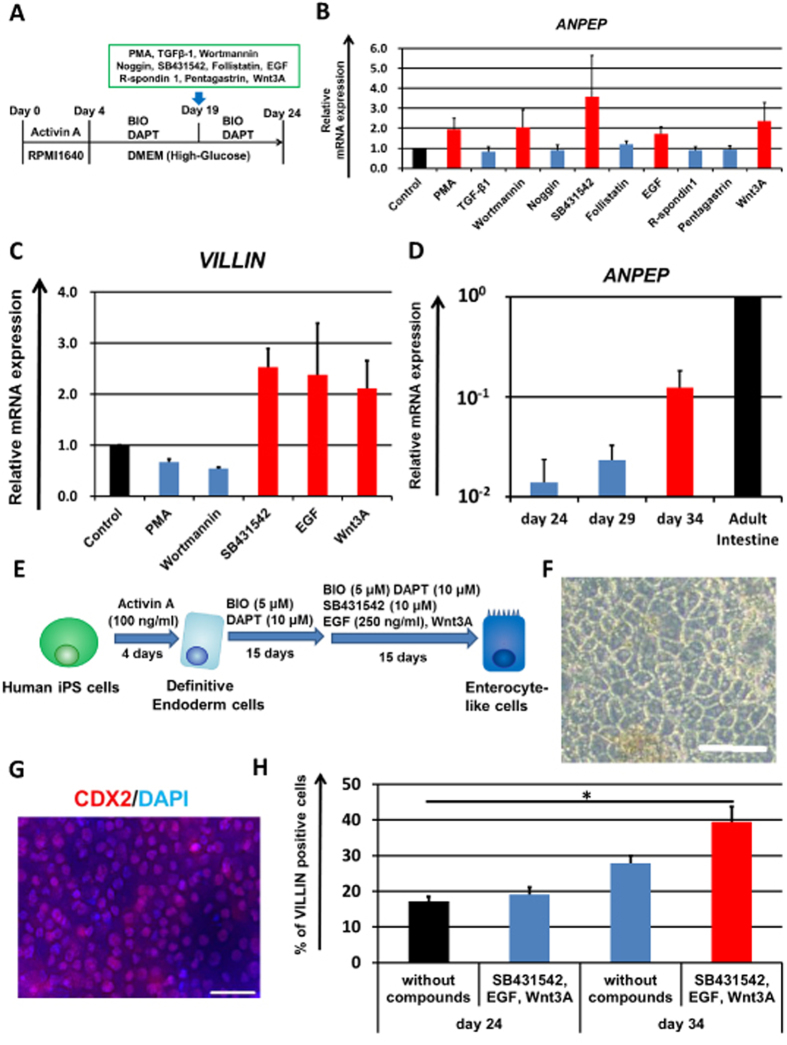
Figure 1. Promotion of enterocyte differentiation by combination treatment with three compounds and differentiation period extension.
(A) The procedure for enterocyte differentiation from human iPS cells by treatment of compounds is presented. From day 19 to 24, the human iPS-derived intestinal cells were treated with the test compounds. (B) The gene expression levels of the enterocyte marker ANPEP in the test compound-treated human iPS-derived intestinal cells were measured by real-time RT-PCR analysis on day 24. On the y axis, the gene expression levels in “Control (untreated hiPS-ELCs)” were taken as 1.0. (C) On day 24, the gene expression levels of the enterocyte marker VILLIN in the PMA, Wortmannin, SB431542, EGF or Wnt3A-treated human iPS-derived intestinal cells were measured by real-time RT-PCR analysis. On the y axis, the gene expression levels in “Control” were taken as 1.0. (D) Temporal gene expression levels of ANPEP in the human iPS cell-derived intestinal cells (day 24, 29, and 34) were measured by real-time RT-PCR analysis. On the y axis, the gene expression levels in Adult Intestine were taken as 1.0. (E) The modified enterocyte differentiation protocol is illustrated. (F) A morphological image of human iPS-derived enterocyte-like cells is represented. Scale bar represents 100 μm. (G) Human iPS cell-derived enterocyte-like cells were assayed for the expression of intestinal marker CDX2 (Red) by immunohistochemistry. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (Blue). Scale bar represents 40 μm. (H) Percentages of VILLIN-positive cells in the SB431542, EGF, and Wnt3A-treated enterocyte-like cells were analyzed by flow cytometry analysis on day 24 and 34. Data are represented as the means ± S.E. (n ≧ 3). Statistical analysis was performed using the unpaired two-tailed student’s t-test. *P < 0.05.