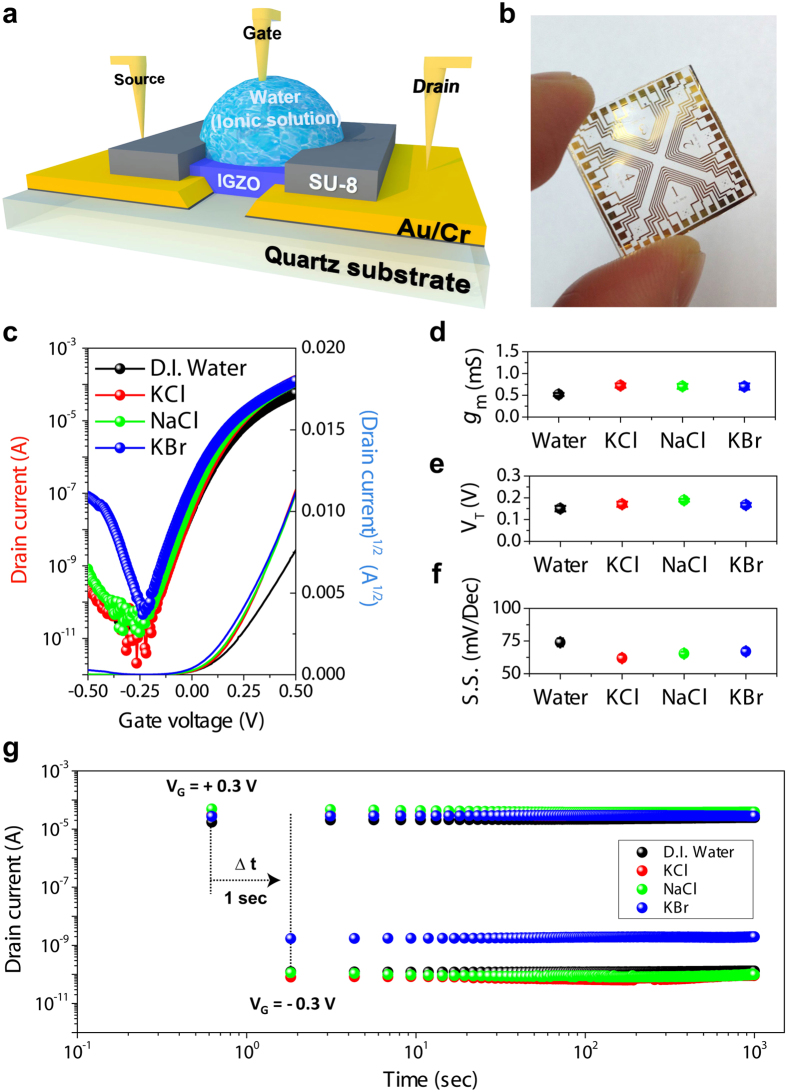
Figure 1. Electrolyte-gated IGZO thin film transistors (IGZO-EGTFTs) using various aqueous dielectrics.
(a) A schematic of aqueous salt EGTFT structure composed of a quartz substrate, source and drain Au/Cr electrode patterns, an IGZO semiconducting layer, an SU-8 passivation well for electrical isolation and solution reservoir containing pure water or salt solutions as dielectric media (from bottom to top). (b) A photographic image of completed IGZO-EGTFT device arrays on a quartz substrate. (c) Representative transfer curves of IGZO EGTFTs using various solutions at VD = +0.5 V. (Black, red, green, and blue lines correspond to DI water, KCl, NaCl, and KBr salt solutions, respectively). Average values of (d) maximum transconductance (defined as gm = ∆ID/∆VG), (e) threshold voltage, and (f) subthreshold swings (S.S.); error bars denote standard deviations over 10 device measurements. (g) Drain current versus time (log scales) plot obtained every 1 s at +0.3 V and −0.3 V of alternating gate biases with +0.5 V of a constant drain voltage over 103 cycles.