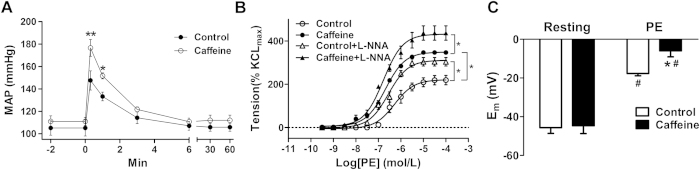
Figure 1. The effect of prenatal caffeine on phenylephrine (PE)-mediated pressor responses, vasoconstrictions, and membrane depolarization in offspring mesenteric arteries (MA).
(A) Mean arterial pressure (MAP) in response to PE (n = 8 each group). 0 min: time for injection of PE. (B) Cumulative dose-response contractions in the MA induced by PE in absence or presence of L-NNA (10−5 mol/L) (n = 8 each group). (C) Depolarization of MA myocytes by 10−5 mol/L PE (n = 14 cells, 6 animals/each group). *P < 0.05, control vs. caffeine; #p < 0.05, comparison for resting membrane potentials in the same group.