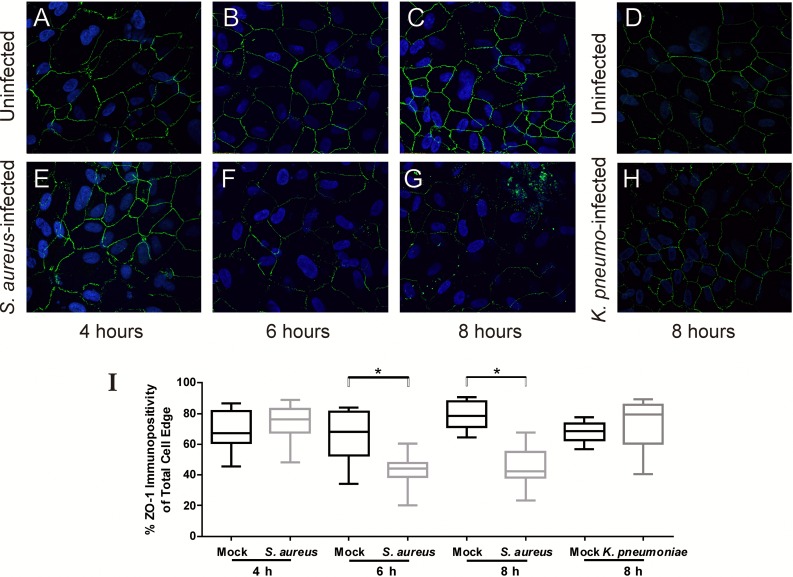
Figure 1.
Staphylococcus aureus induces alterations in ZO-1 immunoreactivity in cultured human RPE cells. Intact monolayers of human RPE cells were infected with S. aureus 8325-4 at a concentration of 104 cfu/mL (MOI = 0.02), stained with anti–ZO-1, and analyzed by immunofluorescence. (A–D) Uninfected RPE cells. (E–G) Retinal pigment epithelial cells at 4, 6, and 8 hours following infection with S. aureus. (H) Retinal pigment epithelial cells at 8 hours following infection with K. pneumoniae. (A–H) ×10 magnification. (I) Results of the quantitative analysis of ZO-1 staining. The y-axes represent % immunopositivity for anti–ZO-1 from five randomly selected cells from each of N ≥ 10 separate fields (6-hour mock-infected RPE cells versus S. aureus infected, P = 0.0007; 8-hour mock-infected RPE cells versus S. aureus infected, P < 0.0001).